Increased Funding for RNA Research
The Small Interfering RNA Market is benefiting from increased funding for RNA research initiatives. Governments and private organizations are recognizing the potential of RNA-based therapies, leading to substantial investments in research and development. For instance, funding for RNA research has seen a significant uptick, with estimates suggesting an increase of over 20% in the last few years. This financial support is crucial for advancing the understanding of RNA biology and the development of novel siRNA therapeutics. As more resources are allocated to this field, the Small Interfering RNA Market is poised for accelerated growth, fostering innovation and the emergence of new therapeutic applications.
Advancements in Delivery Mechanisms
Innovations in delivery mechanisms are playing a crucial role in the evolution of the Small Interfering RNA Market. The effectiveness of siRNA therapeutics is heavily reliant on their ability to reach target cells efficiently. Recent advancements, such as lipid nanoparticles and viral vectors, have shown promise in enhancing the delivery and stability of siRNA molecules. These technologies not only improve the bioavailability of siRNA but also minimize potential side effects. As a result, the market is witnessing a shift towards more sophisticated delivery systems, which could potentially increase the therapeutic efficacy of siRNA-based treatments. The ongoing research in this domain suggests that the Small Interfering RNA Market will continue to benefit from these technological advancements, leading to more successful clinical applications.
Rising Demand for Targeted Therapies
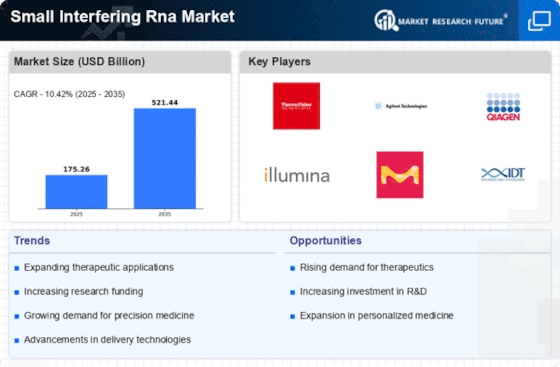
The Small Interfering RNA Market is experiencing a notable surge in demand for targeted therapies, particularly in the treatment of various genetic disorders and cancers. This trend is driven by the increasing recognition of RNA interference as a potent therapeutic strategy. According to recent estimates, the market for RNA-based therapeutics is projected to reach approximately USD 10 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of around 15%. This growth is indicative of the broader acceptance of siRNA technologies in clinical settings, as they offer the potential for high specificity and reduced off-target effects. As healthcare providers and patients alike seek more effective treatment options, the Small Interfering RNA Market is likely to expand significantly, fostering innovation and investment in this promising area.
Growing Focus on Personalized Medicine
The Small Interfering RNA Market is increasingly aligned with the growing focus on personalized medicine. As healthcare shifts towards more individualized treatment approaches, the ability of siRNA to target specific genetic mutations presents a unique opportunity. This trend is particularly evident in oncology, where personalized therapies are becoming the standard of care. The market for personalized medicine is expected to reach USD 2.5 trillion by 2028, indicating a robust growth trajectory. This shift not only enhances patient outcomes but also drives demand for innovative siRNA solutions tailored to individual genetic profiles. Consequently, the Small Interfering RNA Market is likely to see a rise in collaborations between biotech firms and healthcare providers to develop customized therapies that leverage the precision of siRNA technology.
Regulatory Support for RNA Therapeutics
Regulatory bodies are increasingly providing support for the development of RNA therapeutics, which is positively impacting the Small Interfering RNA Market. Streamlined approval processes and clear guidelines for siRNA-based products are encouraging companies to invest in this area. Recent initiatives by regulatory agencies have aimed to facilitate the clinical development of RNA therapies, thereby reducing the time to market. This supportive regulatory environment is likely to enhance the confidence of investors and stakeholders in the Small Interfering RNA Market, leading to a proliferation of new products and therapies. As the landscape evolves, the potential for siRNA technologies to address unmet medical needs becomes more pronounced.