Tokenization of Assets
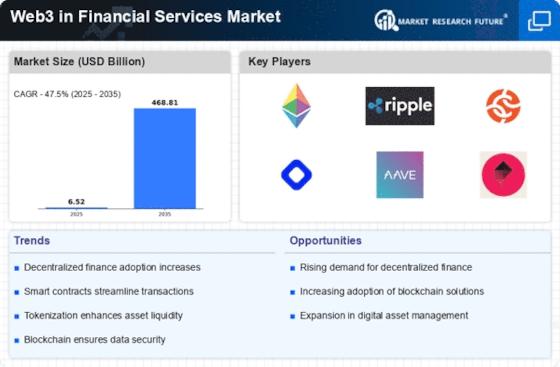
The tokenization of assets represents a transformative trend within the Web3 in Financial Services Market. By converting physical and digital assets into blockchain-based tokens, financial services can enhance liquidity and accessibility. As of October 2025, the market for tokenized assets is projected to reach 10 trillion USD, reflecting a growing interest in this innovative approach. Tokenization allows for fractional ownership, enabling a broader range of investors to participate in markets that were previously inaccessible. This democratization of investment opportunities is likely to drive further adoption of Web3 technologies, as individuals and institutions recognize the potential benefits of tokenized assets. Consequently, the Web3 in Financial Services Market is poised for significant growth as more assets are tokenized and integrated into decentralized platforms.
Decentralized Finance Adoption
The rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms is a pivotal driver in the Web3 in Financial Services Market. DeFi enables users to engage in financial transactions without intermediaries, thereby reducing costs and increasing efficiency. As of October 2025, the total value locked in DeFi protocols has surpassed 100 billion USD, indicating a robust adoption rate. This shift towards decentralized solutions is attracting both retail and institutional investors, who are increasingly seeking alternatives to traditional banking systems. The Web3 in Financial Services Market is witnessing a transformation as DeFi applications proliferate, offering innovative financial products such as lending, borrowing, and yield farming. This trend suggests a fundamental change in how financial services are delivered, potentially reshaping the entire financial landscape.
Enhanced Security and Transparency
Security and transparency are paramount in the Web3 in Financial Services Market, particularly as cyber threats continue to evolve. Blockchain technology, which underpins Web3, offers immutable records and enhanced security features that traditional financial systems often lack. As of October 2025, incidents of data breaches in financial institutions have prompted a shift towards blockchain solutions, which provide a decentralized and tamper-proof environment for transactions. This heightened focus on security is likely to drive the adoption of Web3 technologies, as consumers and businesses alike seek assurance that their financial data is protected. Furthermore, the transparency afforded by blockchain can enhance trust in financial transactions, which is crucial for the growth of the Web3 in Financial Services Market.
Regulatory Evolution and Compliance
The evolving regulatory landscape is a crucial driver in the Web3 in Financial Services Market. As governments and regulatory bodies begin to establish frameworks for blockchain and cryptocurrency, compliance becomes increasingly important for businesses operating in this space. As of October 2025, several jurisdictions have introduced regulations aimed at fostering innovation while ensuring consumer protection. This regulatory clarity is likely to encourage more traditional financial institutions to explore Web3 solutions, as they seek to align with compliance requirements. The establishment of clear guidelines may also enhance investor confidence, which is essential for the growth of the Web3 in Financial Services Market. As regulations continue to evolve, they will shape the development and adoption of Web3 technologies in financial services.
Interoperability of Financial Systems
Interoperability among various financial systems is emerging as a critical driver in the Web3 in Financial Services Market. As different blockchain networks and financial platforms seek to communicate seamlessly, the demand for interoperable solutions is increasing. This trend is evidenced by the development of cross-chain protocols that facilitate transactions across multiple blockchains. As of October 2025, several projects are actively working on enhancing interoperability, which could lead to a more cohesive financial ecosystem. The ability to transfer assets and data across platforms without friction is likely to attract more users to Web3 solutions, thereby accelerating the growth of the Web3 in Financial Services Market. This interconnectedness may also foster innovation, as developers create new applications that leverage the strengths of various blockchain technologies.