Expansion of Offshore Wind Farms
The expansion of offshore wind farms significantly influences the submarine power-cable market in Japan. With the government targeting 10 GW of offshore wind capacity by 2030, the demand for submarine cables to transmit generated electricity to the mainland is expected to rise. This initiative aligns with Japan's commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to sustainable energy sources. The development of these wind farms necessitates advanced submarine cable technology to ensure efficient energy transmission over long distances. As a result, investments in submarine power-cable infrastructure are likely to increase, fostering innovation and competition within the market. The integration of these cables into the energy grid is crucial for achieving Japan's renewable energy goals.
Government Initiatives and Funding
Government initiatives and funding play a pivotal role in shaping the submarine power-cable market in Japan. The Japanese government has introduced various programs aimed at promoting renewable energy and enhancing energy infrastructure. Financial incentives, grants, and subsidies for submarine cable projects are designed to stimulate private sector investment. The government’s commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 further underscores the importance of developing a robust submarine power-cable network. By facilitating public-private partnerships, the government aims to accelerate the deployment of submarine cables, ensuring that the necessary infrastructure is in place to support the growing renewable energy sector. This proactive approach is likely to create a favorable environment for market growth.
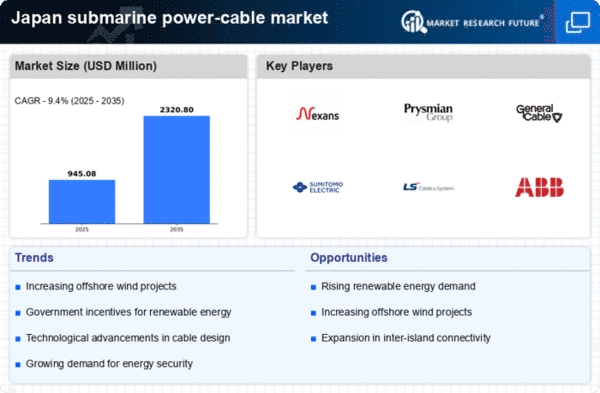
Growing Demand for Energy Security
The submarine power-cable market in Japan is experiencing a notable surge in demand due to the increasing need for energy security. As Japan continues to diversify its energy sources, the reliance on renewable energy, particularly offshore wind, is becoming more pronounced. This shift necessitates robust infrastructure, including submarine cables, to connect remote energy generation sites to urban centers. The government has set ambitious targets for renewable energy, aiming for 36-38% of total energy generation by 2030. This transition is likely to propel investments in submarine power-cable projects, enhancing the market's growth prospects. Furthermore, the need to ensure a stable and reliable energy supply in the face of natural disasters further emphasizes the importance of developing resilient submarine cable networks.
Technological Innovations in Cable Design
Technological innovations in cable design are reshaping the submarine power-cable market in Japan. Advances in materials and manufacturing processes enhance the performance and reliability of submarine cables, making them more suitable for harsh marine environments. Innovations such as improved insulation materials and enhanced cable laying techniques contribute to increased efficiency and reduced installation costs. The market is witnessing a shift towards high-voltage direct current (HVDC) systems, which offer advantages in long-distance power transmission. As Japan invests in cutting-edge technology, the submarine power-cable market is likely to benefit from enhanced capabilities, enabling the integration of renewable energy sources into the national grid more effectively. This trend may lead to a more resilient and efficient energy infrastructure.
Increased Interconnection with Neighboring Countries
Increased interconnection with neighboring countries is emerging as a key driver for the submarine power-cable market in Japan. The country is exploring opportunities to enhance energy trade with regional partners, such as South Korea and Taiwan, through the development of submarine cable links. These interconnections can facilitate the exchange of renewable energy, contributing to energy security and stability in the region. The potential for cross-border electricity trade is expected to drive investments in submarine cable infrastructure, as Japan seeks to optimize its energy resources and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. This trend may lead to a more integrated energy market in East Asia, with Japan playing a central role in regional energy cooperation.