Advancements in Genetic Research
Recent advancements in genetic research are significantly impacting the chronic granulomatous-disease market. Innovations in gene therapy and genetic testing have opened new avenues for treatment and diagnosis. For instance, the development of CRISPR technology has shown promise in correcting the genetic mutations responsible for chronic granulomatous disease. This could potentially lead to curative therapies, which would transform the treatment landscape. Additionally, genetic testing allows for earlier diagnosis, enabling timely intervention and management of the disease. As these technologies continue to evolve, they are likely to enhance the chronic granulomatous-disease market, attracting investment and interest from pharmaceutical companies and research institutions.
Growing Investment in Rare Disease Research
The chronic granulomatous disease market benefits from a surge in investment directed towards rare disease research. In recent years, funding from both public and private sectors has increased, with the National Institutes of Health (NIH) allocating substantial resources to rare diseases, including chronic granulomatous disease. This financial support fosters innovation and accelerates the development of new therapies. Furthermore, the Orphan Drug Act incentivizes pharmaceutical companies to develop treatments for rare diseases, potentially leading to a wider array of options for patients. As investment continues to grow, the chronic granulomatous-disease market is likely to see an influx of novel therapies and improved patient outcomes.
Rising Demand for Specialized Healthcare Services
The chronic granulomatous disease market is seeing increased demand for specialized healthcare services tailored to the needs of affected individuals. As awareness of the disease grows, healthcare providers are recognizing the importance of offering comprehensive care that includes not only medical treatment but also psychological support and patient education. This holistic approach is essential for managing chronic granulomatous disease effectively. Additionally, specialized clinics and treatment centers are emerging, focusing on the unique challenges faced by patients. This trend is likely to drive market growth, as patients seek out these tailored services to improve their quality of life and health outcomes.
Enhanced Regulatory Support for Treatment Approvals
Regulatory bodies in the United States are increasingly providing support for the approval of treatments for rare diseases, including chronic granulomatous disease. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has implemented various initiatives aimed at expediting the review process for orphan drugs. This regulatory environment encourages pharmaceutical companies to invest in the development of new therapies, as the path to market is becoming more streamlined. As a result, The chronic granulomatous disease market is poised for growth, with new treatments potentially entering the market more rapidly. This enhanced regulatory support may lead to improved access to therapies for patients, ultimately benefiting the overall market.
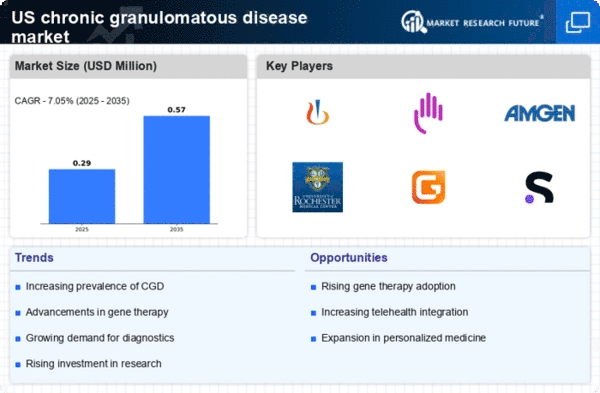
Increasing Prevalence of Chronic Granulomatous Disease
The chronic granulomatous-disease market is experiencing growth due to the rising prevalence of this rare genetic disorder in the United States. Estimates suggest that approximately 1 in 200,000 individuals are affected by chronic granulomatous disease, leading to a growing patient population that requires specialized care. This increase in prevalence drives demand for diagnostic tools and treatment options, thereby expanding the market. Furthermore, as awareness of the disease increases among healthcare professionals and the public, more individuals are likely to seek diagnosis and treatment, further contributing to market growth. Thus, the chronic granulomatous disease market is positioned to benefit from this upward trend in prevalence. Ongoing research and development are necessary to meet the needs of affected individuals.