Top Industry Leaders in the Satellite Market

Strategies Adopted: Key players in the Satellite Market employ various strategies to maintain their competitive edge and capitalize on market opportunities. These strategies include:
Diversification: Companies diversify their product and service offerings across different segments of the satellite industry, including communication satellites, Earth observation satellites, navigation satellites, and satellite-based services, to mitigate risks and expand revenue streams.
Vertical Integration: Vertical integration across the satellite value chain, from satellite design and manufacturing to launch services and ground infrastructure, enables companies to control costs, quality, and schedules, ensuring seamless coordination and delivery of end-to-end solutions.
Strategic Partnerships: Collaborations with satellite operators, government agencies, telecommunications companies, and technology providers help companies access new markets, share resources, and leverage complementary capabilities to address evolving customer needs and market trends.
Technology Innovation: Companies invest in research and development to develop advanced satellite technologies, such as high-throughput satellites, small satellites, electric propulsion systems, and software-defined payloads, to improve performance, flexibility, and affordability of satellite solutions.
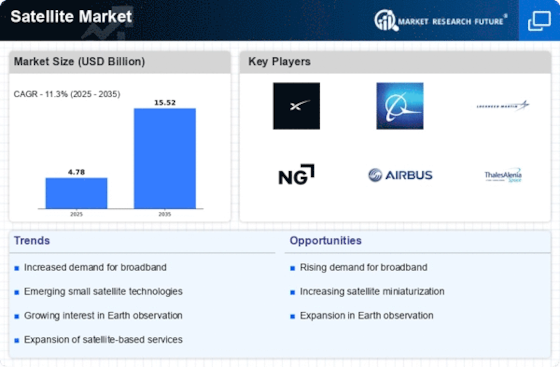
Key Companies in the Satellite market include.
Airbus SAS (Netherlands)
Ball Corporation (US)
Boeing (US)
Eutelsat Communications SA (France)
Intelsat (Luxembourg)
Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd (Israel)
Lockheed Martin Corporation (US)
Northrop Grumman Corporation(US)
Safran (France)
SES SA (Luxembourg)
Space Exploration Technologies Corp (US)
Space Systems/Loral, LLC (US)
Thales Group (France)
Viasat, Inc. (US)
Sierra Nevada Corporation (US)
L3 Harris Technologies (US)
Factors for Market Share Analysis: Several factors contribute to the analysis of market share in the Satellite Market, including:
Satellite Fleet Size and Coverage: The size, coverage, and performance of satellite fleets play a crucial role in determining market share, with companies operating large, geographically diverse satellite constellations capable of delivering high-speed, reliable connectivity and global coverage gaining a competitive advantage.
Customer Relationships: Strong relationships with satellite operators, government agencies, broadcasters, telecommunications providers, and enterprise customers enhance market share by fostering trust, loyalty, and long-term partnerships, with companies offering tailored solutions and responsive customer support gaining a competitive edge.
Pricing and Value Proposition: Competitive pricing, flexible service plans, and value-added features, such as bandwidth management, network optimization, and value-added services, influence market share by addressing cost concerns and delivering differentiated value propositions to customers.
Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with regulatory requirements, spectrum allocations, and licensing procedures is essential for gaining market share and securing contracts in the highly regulated satellite industry, with companies adhering to international standards and best practices gaining credibility and trust among customers and regulators.
New and Emerging Companies: In addition to established players, new and emerging companies are entering the Satellite Market, bringing innovative technologies and business models. These companies often focus on niche segments or disruptive approaches, challenging traditional players and driving innovation in the industry. Some notable new and emerging companies in the market include:
SpaceX
OneWeb
Planet Labs Inc.
Blue Origin
Rocket Lab
Spire Global Inc.
Swarm Technologies Inc.
Capella Space
Relativity Space
Kepler Communications Inc.
Industry News and Current Investment Trends: Recent developments and investment trends in the Satellite Market reflect a growing interest in mega-constellations, satellite internet, Earth observation, and space exploration. Key highlights include:
Satellite Internet Constellations: Companies like SpaceX, OneWeb, and Amazon are launching mega-constellations of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites to provide global broadband internet coverage, offering high-speed connectivity to underserved and remote areas worldwide.
Earth Observation Services: Demand for satellite-based Earth observation services is increasing for applications such as agriculture, forestry, environmental monitoring, disaster management, and urban planning, driving investment in high-resolution imaging, data analytics, and value-added services.
Space Exploration: Companies are investing in space exploration missions, lunar landings, asteroid mining, and Mars colonization projects, fueling innovation, collaboration, and commercialization opportunities in the satellite industry.
Overall Competitive Scenario: The Satellite Market is highly competitive, characterized by technological innovation, market consolidation, and strategic partnerships. Established players leverage their experience, infrastructure, and customer relationships to maintain market leadership, while new entrants disrupt the market with disruptive technologies and business models. As the demand for satellite-based services continues to grow, companies that focus on agility, innovation, and customer-centricity will thrive in the competitive landscape of the Satellite Market.
Satellite Industry Developments
For Instance, June 2021
Airbus Defence and Space has completed and sent the EUTELSAT QUANTUM satellite to its base in Kourou, French Guiana, for launch by Ariane 5. This advancement will revolutionize the commercial satellite industry because of its high customization and flexibility in inter-orbital maneuvers and the expansion of supply services due to unparalleled in-orbit reconfigurability in power, coverage, and frequency.
For Instance, January 2021
Lockheed Martin has been awarded a USD 4.9 billion contract to create upgraded missile warning satellites for the United States Space Force. The satellites will monitor Earth from geosynchronous orbit, 22,000 miles (36,000 km) above the Earth.