Market Trends
Key Emerging Trends in the Molecular Breeding Market
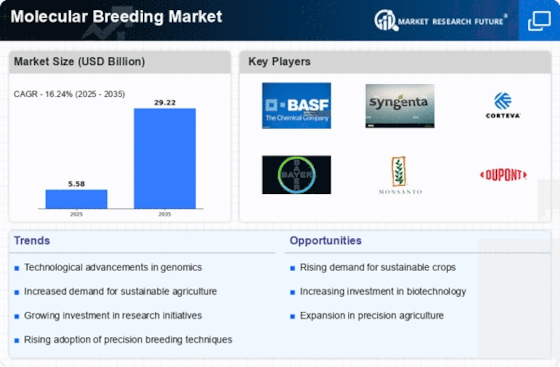
molecular breeding market is experiencing rapid growth and transformative trends driven by advancements in biotechnology, increasing demand for crop improvement solutions, and challenges posed by climate change and global food security issues. Molecular breeding, also known as marker-assisted breeding or genomics-assisted breeding, involves the use of molecular markers and genomic technologies to accelerate the development of improved crop varieties with desirable traits such as yield potential, disease resistance, and stress tolerance. One significant trend is the growing adoption of molecular breeding techniques by plant breeders, seed companies, and agricultural researchers seeking to address the complex challenges facing modern agriculture.
Moreover, advancements in genomics, bioinformatics, and high-throughput sequencing technologies are driving innovation in the molecular breeding market. These tools enable researchers to analyze plant genomes, identify genetic markers associated with important agronomic traits, and accelerate the breeding process by selecting plants with desired genetic profiles at earlier stages of development. Additionally, there's a growing emphasis on genomic selection and predictive breeding models that leverage large-scale genomic data to predict the performance of crop varieties under different environmental conditions, enabling breeders to make more informed decisions and prioritize breeding targets.
Furthermore, the molecular breeding market is benefiting from the broader trend towards sustainable agriculture and precision farming practices. As farmers seek to increase crop yields, reduce input costs, and minimize environmental impact, there's a growing demand for crop varieties developed using molecular breeding techniques that offer improved performance, resource use efficiency, and resilience to biotic and abiotic stresses. Molecular breeding enables breeders to develop crop varieties tailored to specific agroecological zones, production systems, and end-user preferences, resulting in more sustainable and resilient agricultural systems.
Additionally, the molecular breeding market is witnessing increasing demand from emerging economies and regions with expanding agricultural sectors. As global population growth, urbanization, and dietary changes drive demand for food, feed, and fiber, there's a corresponding need for crop varieties adapted to local growing conditions, consumer preferences, and market demands. Molecular breeding technologies offer a cost-effective and efficient means of developing improved crop varieties tailored to the needs of smallholder farmers, commercial growers, and agribusinesses in diverse geographic regions.
However, the molecular breeding market faces challenges such as regulatory constraints, intellectual property issues, and capacity-building constraints in developing countries. Regulatory frameworks governing the use of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and biotechnological tools vary among countries and regions, creating barriers to market entry and commercialization for molecular breeding products. Additionally, intellectual property rights related to genetic resources, molecular markers, and breeding technologies can pose challenges for technology transfer, collaboration, and equitable access to genetic resources and breeding innovations.
Moreover, capacity-building efforts are needed to ensure that farmers, breeders, and agricultural researchers in developing countries have access to the necessary infrastructure, resources, and training to adopt and benefit from molecular breeding technologies. By promoting technology transfer, knowledge sharing, and collaboration among public and private sector stakeholders, the molecular breeding market can contribute to building local breeding capacity, enhancing agricultural productivity, and improving livelihoods in developing countries.


















Leave a Comment