Market Analysis
In-depth Analysis of Maritime Freight Transport Market Industry Landscape
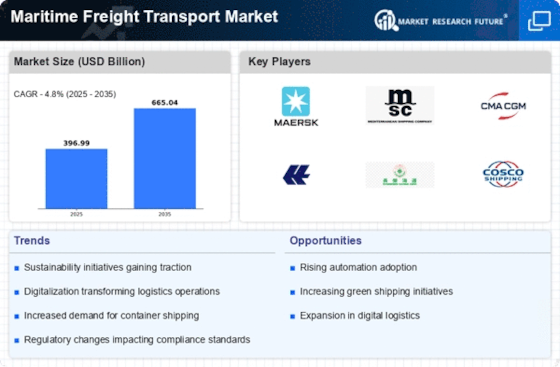
The market dynamics of maritime freight transport reveal a multifaceted landscape shaped by global trade, economic fluctuations, technological advancements, and environmental considerations. Maritime freight transport, often considered the lifeblood of international trade, relies on a complex interplay of factors that influence its growth and evolution. One of the primary drivers of the market is the continuously expanding global trade. As businesses seek to access diverse markets and source materials from different regions, the demand for maritime freight transport services increases. Container shipping, in particular, has become a dominant mode for the transportation of goods, enabling efficient and cost-effective movement across oceans.
Economic conditions and trade policies significantly impact the market dynamics of maritime freight transport. During periods of economic growth, the demand for goods increases, leading to higher shipping volumes. Conversely, economic downturns may result in reduced trade activity, affecting the shipping industry. Trade tensions, tariff adjustments, and changes in international agreements can also influence shipping routes, shipping rates, and overall market conditions, making the industry sensitive to geopolitical developments.
Technological advancements play a crucial role in shaping the dynamics of maritime freight transport. The adoption of digital technologies, such as blockchain, IoT (Internet of Things), and data analytics, enhances the efficiency and transparency of supply chain operations. These technologies provide real-time tracking, optimize route planning, and improve communication between stakeholders, reducing delays and enhancing overall logistics performance. Automation and digitization have also streamlined port operations, cargo handling, and documentation processes, contributing to increased efficiency in maritime logistics.
Environmental sustainability has emerged as a significant consideration within the market dynamics of maritime freight transport. The industry faces increasing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint and adopt greener practices. Efforts to comply with international regulations, such as the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) sulfur emissions limits, drive the industry towards cleaner fuels and the development of eco-friendly technologies. As awareness of climate change grows, consumers and businesses alike are increasingly choosing carriers that prioritize environmental responsibility, influencing the market dynamics.
Competition within the maritime freight transport market is intense, with numerous shipping companies, alliances, and carriers vying for market share. The industry's competitive landscape is shaped by factors such as fleet size, route networks, shipping capacities, and service reliability. Strategic alliances and partnerships among shipping companies are common, allowing them to pool resources, share vessels, and optimize routes. Mergers and acquisitions also play a role in shaping the competitive dynamics, leading to the consolidation of market players.
Challenges within the maritime freight transport industry include overcapacity, volatile fuel prices, geopolitical uncertainties affecting trade routes, and the potential impact of global events on shipping activities. The industry's response to these challenges involves optimizing operational efficiency, investing in sustainable technologies, and adapting to evolving market conditions.

















Leave a Comment