Market Trends
Key Emerging Trends in the Low GWP Refrigerants Market
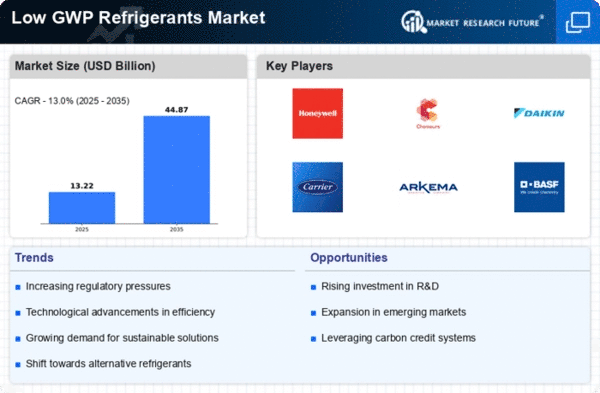
The market for low GWP refrigerants has changed significantly in recent years, reflecting a greater awareness and responsibility to the environment. As environmental concerns grow, companies are seeking alternatives to high GWP refrigerants, which support ozone-depleting chemical releases. This transition is driven by administrative measures like the Kigali Correction to the Montreal Convention, which aims to reduce the production and use of high-GWP hydrofluorocarbons.
The low GWP refrigerants market has seen increased use of standard refrigerants. Normal refrigerants including alkali, CO2, and hydrocarbons have gained popularity due to their low climate impact. Due of its excellent thermodynamic qualities, smelling salts are used in modern refrigeration systems. CO2 is utilized in corporate refrigeration as an eco friendly, low GWP solution. These selections aim to balance execution, energy efficiency, and natural duty. Companies are investing in innovative work to provide details that meet administrative norms and cooling system requirements.
Low GWP refrigerant markets prioritize energy productivity. As companies reduce their carbon footprint and comply with strict energy productivity criteria, demand for low-GWP refrigerants that improve energy efficiency is rising. Retrofit and new establishments are favoring low-GWP refrigerants that improve framework efficiency and performance.
Unofficial rules and peaceful accords shape the low GWP refrigerant business. Countries are adapting to global environmental change efforts, creating an optimal setting for low-GWP solutions. The market is moving forward due to regulations promoting the use of eco-friendly refrigerants, with companies adapting to retain their sustainability.
Despite administrative drivers, customer preferences and business manageability goals affect market variables. Buyers are increasingly aware of products' environmental impact and favor eco-friendly companies. This change in buyer sentiment is prompting companies to use low-GWP refrigerants in their products and services, growing the market.The market for low GWP refrigerants has changed significantly in recent years, reflecting a greater awareness and responsibility to the environment. As environmental concerns grow, companies are seeking alternatives to high GWP refrigerants, which support ozone-depleting chemical releases. This transition is driven by administrative measures like the Kigali Correction to the Montreal Convention, which aims to reduce the production and use of high-GWP hydrofluorocarbons.
The low GWP refrigerants market has seen increased use of standard refrigerants. Normal refrigerants including alkali, CO2, and hydrocarbons have gained popularity due to their low climate impact. Due of its excellent thermodynamic qualities, smelling salts are used in modern refrigeration systems. CO2 is utilized in corporate refrigeration as an eco friendly, low GWP solution. These selections aim to balance execution, energy efficiency, and natural duty. Companies are investing in innovative work to provide details that meet administrative norms and cooling system requirements.
Low GWP refrigerant markets prioritize energy productivity. As companies reduce their carbon footprint and comply with strict energy productivity criteria, demand for low-GWP refrigerants that improve energy efficiency is rising. Retrofit and new establishments are favoring low-GWP refrigerants that improve framework efficiency and performance.
Unofficial rules and peaceful accords shape the low GWP refrigerant business. Countries are adapting to global environmental change efforts, creating an optimal setting for low-GWP solutions. The market is moving forward due to regulations promoting the use of eco-friendly refrigerants, with companies adapting to retain their sustainability.
Despite administrative drivers, customer preferences and business manageability goals affect market variables. Buyers are increasingly aware of products' environmental impact and favor eco-friendly companies. This change in buyer sentiment is prompting companies to use low-GWP refrigerants in their products and services, growing the market.

















Leave a Comment