Regulatory Support for New Treatments
Regulatory support for the approval of new treatments is a vital driver for the overactive bladder-treatment market. In Italy, the regulatory framework encourages the introduction of innovative therapies, which can expedite the availability of new medications to patients. The Italian Medicines Agency (AIFA) plays a crucial role in evaluating and approving new treatments, ensuring that effective options are accessible to those in need. This supportive environment is likely to foster innovation within the pharmaceutical sector, leading to the development of advanced therapies for OAB. As a result, the overactive bladder-treatment market may witness accelerated growth, driven by the timely introduction of new and effective treatment modalities.
Advancements in Pharmaceutical Research
Innovations in pharmaceutical research are significantly impacting the overactive bladder-treatment market. Recent advancements have led to the development of new medications that offer improved efficacy and reduced side effects compared to traditional treatments. For instance, the introduction of novel antimuscarinic agents and beta-3 adrenergic agonists has provided patients with more options for managing their symptoms. The Italian pharmaceutical industry is actively investing in research and development, with expenditures reaching approximately €1.5 billion annually. This investment is likely to yield new therapies that could enhance patient outcomes and drive market growth. As a result, the overactive bladder-treatment market is poised for expansion, with a focus on innovative solutions that address the unmet needs of patients.
Growing Awareness and Education Initiatives
In Italy, increasing awareness and education initiatives regarding overactive bladder are crucial drivers for the treatment market. Healthcare organizations and advocacy groups are actively promoting understanding of OAB symptoms and treatment options, which is likely to lead to higher diagnosis rates. Campaigns aimed at educating both healthcare professionals and the general public are essential in reducing stigma associated with the condition. As awareness grows, more individuals are likely to seek medical advice and treatment, thereby expanding the patient pool. This trend suggests that the overactive bladder-treatment market will experience growth as more patients become informed about their options and pursue effective management strategies.
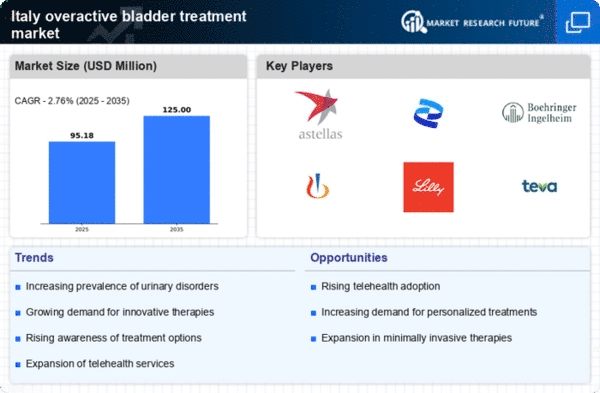
Increasing Prevalence of Overactive Bladder
The rising incidence of overactive bladder (OAB) in Italy is a primary driver for the overactive bladder-treatment market. Recent studies indicate that approximately 16% of the adult population in Italy experiences symptoms of OAB, which translates to millions of individuals seeking effective treatment options. This growing patient base is likely to stimulate demand for various therapeutic interventions, including pharmacological treatments and behavioral therapies. As awareness of OAB increases, healthcare providers are more inclined to diagnose and treat this condition, further propelling market growth. The overactive bladder-treatment market is expected to expand as more patients seek relief from the debilitating symptoms associated with OAB, thereby creating opportunities for pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers to innovate and offer tailored solutions.
Aging Population and Associated Health Issues
Italy's aging population is a significant factor influencing the overactive bladder-treatment market. As the demographic shifts towards an older age group, the prevalence of OAB is expected to rise, given that older adults are more susceptible to urinary disorders. Current statistics indicate that nearly 30% of individuals aged 65 and older in Italy report symptoms of OAB. This demographic trend is likely to increase the demand for effective treatment solutions tailored to the needs of older patients. Consequently, the overactive bladder-treatment market is anticipated to grow as healthcare providers focus on addressing the unique challenges faced by this population, including comorbidities and polypharmacy.