Increased Adoption of Automation
The trend towards automation in various industries is significantly influencing the hydraulic pumps market. Automation enhances operational efficiency and reduces labor costs, leading to a higher demand for hydraulic systems that can be integrated into automated machinery. Industries such as manufacturing and agriculture are increasingly utilizing hydraulic pumps to power automated equipment, which is expected to drive market growth. The hydraulic pumps market is likely to benefit from this shift, as companies seek to optimize their processes and improve productivity through advanced hydraulic solutions.
Growing Focus on Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency has become a critical consideration across industries, prompting a shift towards hydraulic pumps that offer improved performance with lower energy consumption. The hydraulic pumps market is responding to this trend by developing innovative products that meet stringent energy standards. For instance, variable displacement pumps are gaining traction due to their ability to adjust flow rates based on demand, thereby reducing energy waste. This focus on energy-efficient solutions is expected to propel the hydraulic pumps market forward, as businesses increasingly prioritize sustainability and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
Rising Demand in Construction Sector
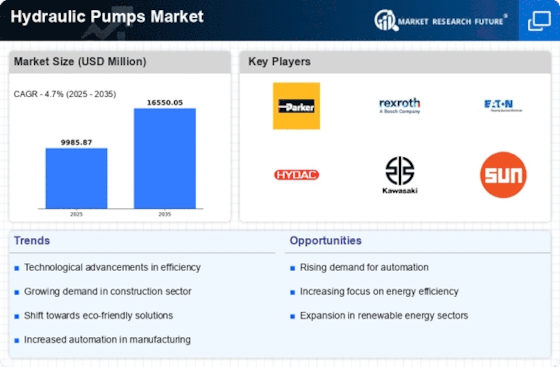
The construction sector is experiencing a notable surge in demand for hydraulic pumps, driven by ongoing infrastructure projects and urbanization. Hydraulic pumps are integral to various construction machinery, including excavators and cranes, which are essential for efficient operations. The hydraulic pumps market is projected to witness a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 5.5% over the next few years, reflecting the increasing reliance on hydraulic systems in construction applications. As cities expand and new buildings emerge, the need for reliable hydraulic pumps becomes paramount, indicating a robust growth trajectory for the hydraulic pumps market.
Expansion of Renewable Energy Projects
The expansion of renewable energy projects, such as wind and solar power, is creating new opportunities for the hydraulic pumps market. Hydraulic systems are essential in various applications within these sectors, including the operation of hydraulic turbines and solar tracking systems. As investments in renewable energy continue to rise, the demand for hydraulic pumps that can withstand diverse environmental conditions is likely to increase. This trend suggests a promising outlook for the hydraulic pumps market, as it aligns with the global shift towards sustainable energy solutions.
Technological Innovations in Hydraulic Systems
Technological innovations are reshaping the hydraulic pumps market, with advancements in materials and design leading to enhanced performance and reliability. The introduction of smart hydraulic pumps equipped with IoT capabilities allows for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs. These innovations are particularly appealing to industries that rely heavily on hydraulic systems, such as manufacturing and construction. As companies seek to leverage technology for improved efficiency, the hydraulic pumps market is poised for growth, driven by the demand for cutting-edge hydraulic solutions.