Growing Biopharmaceutical Sector
The biopharmaceutical sector in the GCC is experiencing notable growth, which is likely to drive the recombinant proteins market. With an increasing number of biopharmaceutical companies establishing operations in the region, the demand for recombinant proteins is expected to rise. The GCC governments are actively promoting biotechnology initiatives, which may lead to an estimated growth rate of 10-15% in the biopharmaceutical sector over the next few years. This growth is anticipated to create a robust market for recombinant proteins, as they are essential for the development of therapeutic agents and vaccines. Furthermore, the establishment of research and development facilities in the GCC is likely to enhance the production capabilities of recombinant proteins, thereby supporting the overall market expansion.
Advancements in Genetic Engineering
Recent advancements in genetic engineering techniques are poised to significantly impact the recombinant proteins market. Innovations such as CRISPR and synthetic biology are enabling more efficient production of recombinant proteins, which may lead to reduced costs and improved yields. In the GCC, research institutions are increasingly adopting these technologies, which could enhance the region's competitiveness in the global market. The ability to produce high-quality recombinant proteins at lower costs may attract investments and partnerships, further stimulating market growth. As the demand for biopharmaceuticals continues to rise, the integration of advanced genetic engineering methods is likely to play a crucial role in meeting this demand within the recombinant proteins market.
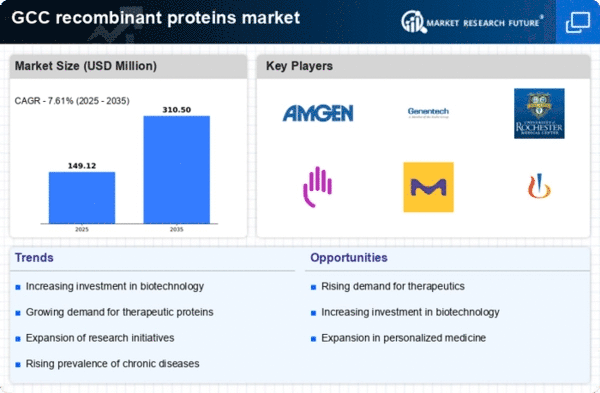
Rising Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases in the GCC is driving the demand for innovative therapeutic solutions, thereby impacting the recombinant proteins market. Conditions such as diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular diseases are on the rise, necessitating the development of effective treatments. Recombinant proteins play a vital role in the production of biologics used for treating these diseases. According to recent health statistics, the GCC countries are experiencing a 20% increase in chronic disease cases annually, which may lead to a corresponding rise in the demand for recombinant proteins. This trend suggests that the recombinant proteins market is likely to expand as healthcare providers seek advanced therapies to address these growing health challenges.
Regulatory Support for Biotech Innovations
Regulatory frameworks in the GCC are increasingly supportive of biotechnology innovations, which is likely to benefit the recombinant proteins market. Governments are streamlining approval processes for biopharmaceutical products, thereby facilitating faster market entry for new recombinant proteins. This regulatory support is essential for fostering a conducive environment for research and development, as well as for attracting foreign investments. The GCC's commitment to enhancing its biotechnology sector is evident in its initiatives to align with international standards, which may further boost the confidence of investors and stakeholders. As a result, the recombinant proteins market could experience accelerated growth due to the favorable regulatory landscape.
Increasing Focus on Research and Development
The GCC region is witnessing a heightened focus on research and development (R&D) in the life sciences, which is expected to bolster the recombinant proteins market. Governments are allocating substantial funding to support R&D initiatives, particularly in biotechnology and pharmaceuticals. This investment is likely to lead to the discovery of new recombinant proteins and their applications in various therapeutic areas. For instance, the GCC countries aim to increase their R&D spending to 1.5% of GDP by 2030, which may significantly enhance the innovation landscape. As a result, the recombinant proteins market could benefit from a steady pipeline of new products and technologies, fostering growth and diversification.