Growing Demand for Personalized Medicine
The shift towards personalized medicine is significantly influencing the Autoimmune Gastrointestinal Dysmotility Market. Patients increasingly seek tailored treatment plans that consider their unique genetic and biochemical profiles. This trend is reflected in the rising number of clinical trials focused on personalized therapies for autoimmune disorders, with over 1,000 trials currently registered. Such an approach not only enhances treatment efficacy but also minimizes adverse effects, thereby improving patient adherence to therapy. As healthcare systems adapt to this paradigm shift, the Autoimmune Gastrointestinal Dysmotility Market is likely to see a surge in demand for customized treatment options that address the specific needs of individuals suffering from gastrointestinal dysmotility.
Rising Prevalence of Autoimmune Disorders
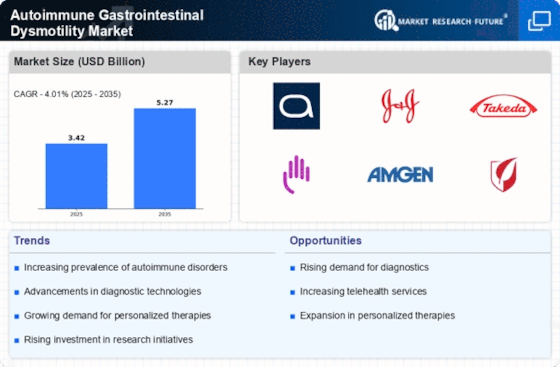
The increasing prevalence of autoimmune disorders is a pivotal driver for the Autoimmune Gastrointestinal Dysmotility Market. As more individuals are diagnosed with conditions such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis, the incidence of gastrointestinal dysmotility associated with these disorders appears to rise. Recent estimates suggest that autoimmune diseases affect approximately 5-8% of the population, leading to a growing demand for specialized treatments and management strategies. This trend indicates a potential expansion in the market, as healthcare providers seek effective solutions to address the gastrointestinal complications that accompany these conditions. Consequently, the Autoimmune Gastrointestinal Dysmotility Market is likely to experience heightened interest from pharmaceutical companies and researchers aiming to develop targeted therapies.
Increased Collaboration Between Stakeholders
Collaboration among various stakeholders, including healthcare providers, researchers, and pharmaceutical companies, is emerging as a key driver for the Autoimmune Gastrointestinal Dysmotility Market. Such partnerships facilitate the sharing of knowledge and resources, which can accelerate the development of new therapies and improve patient care. Recent initiatives have shown that collaborative research efforts can lead to breakthroughs in understanding the pathophysiology of autoimmune gastrointestinal dysmotility. This collaborative spirit is likely to foster innovation and enhance the overall effectiveness of treatment strategies, thereby positively impacting the Autoimmune Gastrointestinal Dysmotility Market.
Increased Investment in Research and Development
Investment in research and development (R&D) is a crucial driver for the Autoimmune Gastrointestinal Dysmotility Market. Pharmaceutical companies and biotech firms are increasingly allocating resources to explore innovative treatment options for autoimmune-related gastrointestinal issues. This trend is underscored by the fact that R&D spending in the healthcare sector has seen a steady increase, with estimates indicating that it could reach over 200 billion USD annually by 2026. Such financial commitment fosters the discovery of novel therapies and diagnostic tools, which may enhance patient outcomes and expand treatment options. As a result, the Autoimmune Gastrointestinal Dysmotility Market stands to benefit from advancements in medical science, potentially leading to more effective management of these complex conditions.
Advancements in Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
The rise of telemedicine and remote monitoring technologies is transforming the landscape of the Autoimmune Gastrointestinal Dysmotility Market. These innovations facilitate better patient management and follow-up care, particularly for those with chronic conditions. Recent data indicates that telehealth usage has surged, with a reported increase of over 150% in consultations for gastrointestinal issues. This shift allows healthcare providers to monitor patients' symptoms and treatment responses more effectively, leading to timely interventions. Consequently, the Autoimmune Gastrointestinal Dysmotility Market is poised to benefit from enhanced patient engagement and improved access to care, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.