Market Trends
Key Emerging Trends in the Wearable Injectors Market
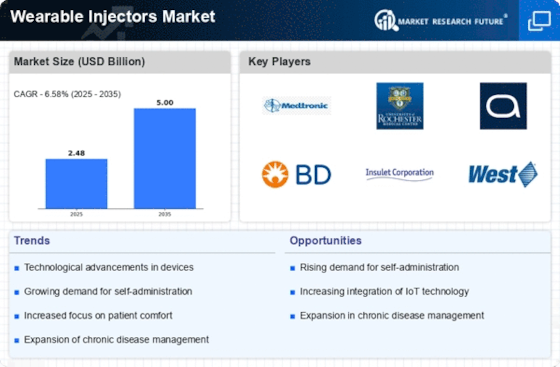
The market of the wearable injectors is experiencing profound changes in line with the growing use of newer and highly efficient drug delivery tools and the need for simpler and more patient-centered approaches to pain management. One of the major tendencies is the increasing preference toward subcutaneous and wearable injectors by the patients who self-administer their drugs. With the help of these devices, people who require a particular drug can now do the job at home, thereby limiting the frequency of visits to medical institutions. This is particularly relevant in chronic disease management where patients can have greater influence in work with their healthcare providers on their treatment routes, therefore ensuring adhering to their regimens and improving health overall.
As well, the smart and connected wearable injectors are being brought into the vogue. These devices are embedded with the connectivity functions enabling patients, and doctors to be tracked for medication adherence, dosage history, and patient-specific body parameters. This tendency complements the overall action to develop digital health options and utilize the data related to patient care and treatment that is optimized. Such devices (smart wearable injectors) are of great advantage to people particularly those with chronic illnesses because they offer real-time data and thus efficient preventive care.
Moreover, the arena of wearable injectors also views new design ideas and advancements. Alongside the manufacturers, there is technology coming out that is smaller, more discreet and user-friendly, thus, in total, enhance the patient experience. Technology including easy-to-use interfaces, audible reminders and ergonomic design play a role in use of wearable injectors across patients in all age groups and in those of different degrees of proficiency in technology. Thus, the main aims of this trend are centered on the idea that better user-oriented design can lead to positive patient attitudes to the utilization of wearable injector technologies.
In addition to this, there is a substantial trend about the design of injectors for slowly viscous drugs and biologicals that can be used by patients themselves at home. Injectors belonging to the old school may be facing problems in delivering thick formulations but because of the advanced mechanics and materials of wearable injectors, these injectors are capable of administering high viscosity medicines. The development of automation and multidose injection systems has followed the rise of biologics and injectable treatments, thus providing a flexible solution for the administration of different types of drugs through one delivery method.
Other big trend is the increasing use of wearable injector to other therapeutic injections. Initially invented for the insulin management in patients with diabetes mellitus, wearable injectors are now under development and deployed for the administration of drugs in other spheres such as oncology, cardiovascular diseases, and autoimmune disorders among others. This diversification mirrors the blankness in the applications of wearable injector technology and the possibility of its use in different medical subgroups.

















Leave a Comment