Rising Demand for Personalized Medicine
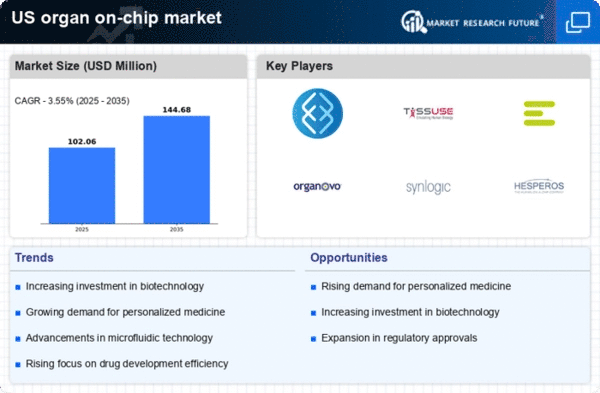
The organ on-chip market is experiencing a notable surge in demand for personalized medicine, driven by the need for tailored therapeutic solutions. As healthcare shifts towards individualized treatment plans, organ-on-chip technologies offer a promising avenue for drug testing and disease modeling. This market segment is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 25% from 2025 to 2030, reflecting the increasing interest in precision medicine. The ability to simulate human organ responses in vitro allows for more accurate predictions of drug efficacy and safety, thereby reducing the reliance on animal testing. Consequently, the organ on-chip market is positioned to play a pivotal role in the development of personalized therapies, aligning with the broader trend of patient-centric healthcare.
Growing Focus on Reducing Animal Testing
The organ on-chip market is significantly influenced by the growing emphasis on reducing animal testing in research and development. Regulatory bodies and ethical considerations are pushing for alternatives that can provide reliable data without the ethical dilemmas associated with animal experimentation. The organ-on-chip technology offers a viable solution by providing human-relevant data that can predict drug responses more accurately. In 2025, it is estimated that the market for alternatives to animal testing will reach $3 billion, highlighting the potential for organ-on-chip systems to capture a substantial share of this market. This shift not only aligns with ethical standards but also enhances the organ on-chip market by promoting innovative testing methods.
Increased Investment in Biotech Research
Investment in biotechnology research is a significant driver for the organ on-chip market. With funding from both public and private sectors, research institutions are increasingly adopting organ-on-chip technologies to enhance drug discovery and development processes. In 2025, the US biotech sector is expected to receive over $50 billion in investments, with a substantial portion allocated to innovative technologies like organ-on-chip systems. These investments facilitate the advancement of sophisticated models that mimic human physiology, thereby improving the accuracy of preclinical testing. As a result, the organ on-chip market is likely to benefit from this influx of capital, fostering innovation and accelerating the commercialization of new therapeutic solutions.
Emerging Applications in Drug Development
The organ on-chip market is witnessing a rise in emerging applications within drug development, which is reshaping the landscape of pharmaceutical research. These systems are being utilized for high-throughput screening, toxicity testing, and disease modeling, offering a more efficient alternative to traditional methods. In 2025, the market for drug development technologies is expected to exceed $40 billion, with organ-on-chip systems capturing a growing share due to their ability to provide real-time data on drug interactions. This trend indicates a shift towards more efficient and effective drug development processes, positioning the organ on-chip market as a critical player in the future of pharmaceutical innovation.
Advancements in Microfabrication Techniques
Advancements in microfabrication techniques are propelling the organ on-chip market forward. These innovations enable the creation of more complex and functional organ models that closely replicate human organ systems. Techniques such as 3D printing and soft lithography are being utilized to develop organ-on-chip devices with enhanced capabilities. As of 2025, the market for microfabrication technologies is projected to grow by 20%, indicating a robust interest in developing sophisticated organ-on-chip systems. This progress allows researchers to create multi-organ systems that can simulate interactions between different organ types, thereby providing a more comprehensive understanding of human biology. Consequently, the organ on-chip market stands to gain from these technological advancements, enhancing its relevance in biomedical research.