Increased Healthcare Expenditure
Rising healthcare expenditure in the US is a significant factor influencing the inflammatory bowel-disease-treatment market. As healthcare budgets expand, there is a greater allocation of resources towards the management of chronic diseases, including IBD. This trend is reflected in the increasing investment in advanced treatment options and patient care programs. According to recent data, healthcare spending in the US is projected to reach $6 trillion by 2027, which may facilitate the development and accessibility of innovative therapies for IBD. Enhanced funding for research initiatives and patient support services is likely to contribute to the overall growth of the market.
Regulatory Support for New Treatments
Regulatory bodies in the US are playing a crucial role in shaping the inflammatory bowel-disease-treatment market. The expedited approval processes for new therapies, particularly those addressing unmet medical needs, are encouraging pharmaceutical companies to invest in IBD treatments. Initiatives such as the FDA's Breakthrough Therapy designation facilitate faster access to innovative therapies for patients. This regulatory support not only accelerates the introduction of new drugs but also fosters competition among manufacturers, potentially leading to more affordable treatment options. As a result, the market is likely to benefit from a diverse range of therapies that cater to the varying needs of IBD patients.
Advancements in Pharmaceutical Research
Innovations in pharmaceutical research are significantly impacting the inflammatory bowel-disease-treatment market. The development of new drug formulations and delivery systems has led to more effective therapies with improved safety profiles. For instance, the introduction of biosimilars has provided cost-effective alternatives to existing biologics, potentially increasing patient access to treatment. Furthermore, ongoing clinical trials are exploring novel compounds that target specific pathways involved in IBD, which may lead to breakthroughs in treatment. The investment in research and development by pharmaceutical companies is expected to drive market growth, as new therapies emerge to meet the diverse needs of patients suffering from IBD.
Growing Awareness and Education Initiatives
The increasing awareness of inflammatory bowel disease among the general public and healthcare professionals is a vital driver for the inflammatory bowel-disease-treatment market. Educational campaigns aimed at both patients and providers are enhancing understanding of IBD symptoms, treatment options, and the importance of early intervention. This heightened awareness is likely to lead to earlier diagnoses and increased treatment uptake. Organizations dedicated to IBD advocacy are actively promoting research funding and patient support, which may further stimulate market growth. As more individuals recognize the impact of IBD on their lives, the demand for effective treatment solutions is expected to rise.
Growing Prevalence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
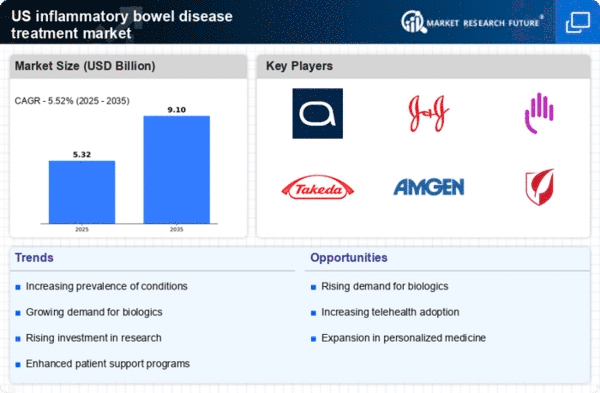
The rising incidence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in the US is a primary driver for the inflammatory bowel-disease-treatment market. Recent estimates indicate that approximately 1.6 million Americans are affected by IBD, with conditions such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis becoming increasingly common. This growing patient population necessitates the development and availability of effective treatment options. As awareness of IBD increases, more individuals seek medical attention, leading to higher demand for therapies. The market is projected to expand as healthcare providers focus on innovative treatments to manage these chronic conditions, thereby enhancing patient quality of life and reducing healthcare costs associated with complications.