Rising Incidence of Neurological Disorders
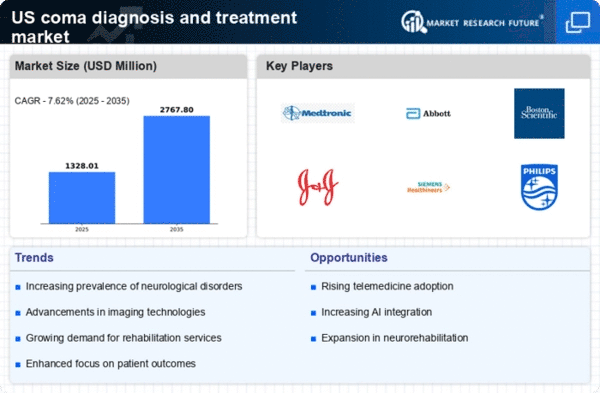
The increasing prevalence of neurological disorders in the US is a primary driver for the coma diagnosis-and-treatment market. Conditions such as traumatic brain injury, stroke, and neurodegenerative diseases contribute significantly to the number of patients experiencing coma. According to the CDC, approximately 795,000 people in the US experience a stroke annually, with a notable percentage leading to coma. This rising incidence necessitates advanced diagnostic tools and treatment options, thereby propelling market growth. The demand for effective management of these conditions is likely to drive investments in research and development, enhancing the capabilities of healthcare providers in the coma diagnosis-and-treatment market.
Increased Funding for Neuroscience Research
In the US, there is a growing emphasis on funding for neuroscience research, which is a vital driver for the coma diagnosis-and-treatment market. Government agencies and private organizations are investing heavily in research initiatives aimed at understanding brain function and developing new treatment modalities. For instance, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) allocated over $3 billion for brain research in recent years, which supports advancements in coma management. This influx of funding not only fosters innovation but also encourages collaboration among researchers, clinicians, and technology developers, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness of treatments available in the coma diagnosis-and-treatment market.
Rising Awareness and Education on Brain Health
There is a notable increase in awareness and education regarding brain health among the general public and healthcare professionals, which serves as a significant driver for the coma diagnosis-and-treatment market. Campaigns aimed at educating individuals about the signs and symptoms of neurological disorders are becoming more prevalent. This heightened awareness encourages early intervention and timely diagnosis, which are critical in coma cases. Furthermore, healthcare providers are increasingly focusing on training programs that emphasize the importance of recognizing comatose states. As awareness continues to grow, the demand for effective diagnostic and treatment solutions in the coma diagnosis-and-treatment market is likely to rise.
Technological Innovations in Monitoring Systems
Technological advancements in monitoring systems are transforming the coma diagnosis-and-treatment market. Innovations such as continuous EEG monitoring and advanced neuroimaging techniques enable healthcare professionals to assess brain activity and identify the depth of coma more accurately. the integration of these technologies improves patient outcomes, as timely and precise diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. the neurodiagnostic devices market is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 8% over the next few years, indicating a robust demand for these innovations. As hospitals and clinics adopt these advanced systems, the coma diagnosis-and-treatment market is expected to expand significantly.
Aging Population and Associated Health Challenges
the aging population in the US is contributing to an increased demand for coma diagnosis and treatment. As individuals age, they become more susceptible to conditions that can lead to coma, such as strokes and traumatic injuries. The US Census Bureau projects that by 2030, approximately 20% of the population will be 65 years or older, which is likely to escalate the incidence of comatose states. This demographic shift necessitates a robust healthcare infrastructure capable of addressing the complexities associated with coma management. Consequently, the coma diagnosis-and-treatment market is poised for growth as healthcare systems adapt to meet the needs of this aging population.