Increased Focus on Preventive Healthcare
The shift towards preventive healthcare is influencing the carotid artery-disease market. As awareness of cardiovascular health rises, more individuals are seeking regular screenings and preventive measures. Initiatives by health organizations and government agencies promote lifestyle modifications and early detection of risk factors associated with carotid artery disease. This trend is reflected in the growing market for preventive services, which is expected to expand at a rate of approximately 5% annually. Consequently, the emphasis on prevention is likely to drive demand for diagnostic tools and treatment options within the carotid artery-disease market.
Rising Incidence of Carotid Artery Disease
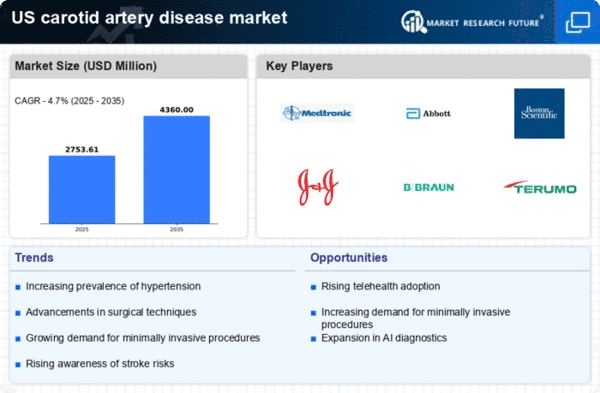
The increasing prevalence of carotid artery disease in the US is a primary driver for the carotid artery-disease market. Factors such as an aging population, lifestyle choices, and comorbidities like hypertension and diabetes contribute to this rise. According to the CDC, approximately 18 million adults in the US have coronary artery disease, which often correlates with carotid artery issues. This growing patient population necessitates enhanced diagnostic and therapeutic options, thereby expanding the market. As healthcare providers focus on early detection and management, the demand for innovative treatments and interventions is likely to surge, further propelling the carotid artery-disease market.
Advancements in Medical Imaging Technologies
Innovations in medical imaging technologies are significantly impacting the carotid artery-disease market. Enhanced imaging modalities, such as high-resolution ultrasound, CT angiography, and MRI, allow for more accurate diagnosis and assessment of carotid artery conditions. These advancements facilitate timely interventions, which are crucial for preventing strokes and other complications. The market for imaging technologies is projected to grow, with estimates suggesting a CAGR of around 6% over the next few years. As healthcare providers increasingly adopt these technologies, the carotid artery-disease market is expected to benefit from improved patient outcomes and increased procedural volumes.
Growing Investment in Healthcare Infrastructure
The expansion of healthcare infrastructure in the US is a significant driver for the carotid artery-disease market. Increased funding for hospitals and outpatient facilities enhances the availability of advanced diagnostic and treatment options. The US government has allocated substantial resources to improve healthcare access, particularly in underserved areas. This investment is likely to lead to a rise in the number of procedures performed for carotid artery disease, thereby boosting market growth. Furthermore, the establishment of specialized centers for vascular health may enhance patient care and outcomes, further stimulating the carotid artery-disease market.
Emerging Biologics and Pharmacological Treatments
The development of new biologics and pharmacological treatments is reshaping the carotid artery-disease market. Innovative therapies targeting inflammation and plaque stabilization are gaining traction, offering potential alternatives to traditional surgical interventions. The market for these advanced treatments is projected to grow significantly, with estimates indicating a potential increase of 8% in the next few years. As clinical trials yield promising results, healthcare providers may increasingly adopt these therapies, thereby enhancing patient management strategies in the carotid artery-disease market.