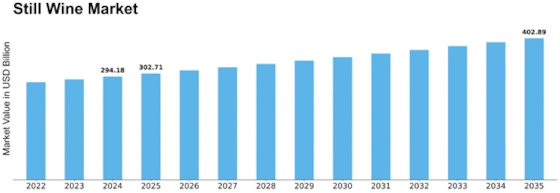
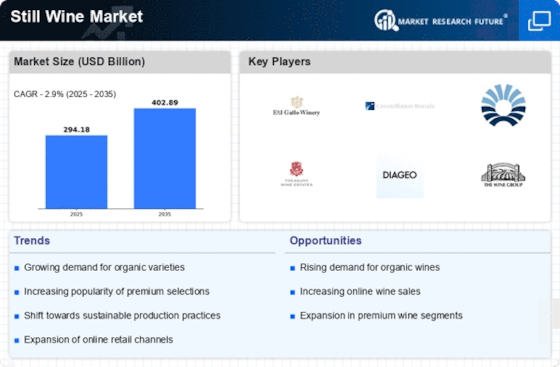
Still Wine Size
Still Wine Market Growth Projections and Opportunities
A variety of factors govern the still wine business, affecting things coming from production to distribution through consumer tastes and worldwide trends. Vineyards' geographical location is an important factor to consider. Environment and the state of the soil play an important influence in grape growing, influencing the quality and qualities of the finished product. Regions with ideal circumstances, such as Bordeaux from France and Napa Valley within the United States, frequently create wines with distinct characteristics, giving their goods a local identity.
Another important consideration is a worldwide economic landscape. Economic conditions have a direct impact on the buying power of consumers and discretionary expenditure on non-essential commodities such as wine. During economic downturns, customers may prefer more cheap choices, resulting in a shift in demand for lower-cost still wines. In contrast, during moments of economic success, customers may be more likely to try premium especially luxury still wines. Technological improvements also influence the still wine business.
Advances involving vineyard management, winemaking procedures, and packaging technologies can increase efficiency, lower costs, and improve product quality. For example, using precision farming and information analytics within vineyard management enables producers to improve grape production, resulting in higher-quality grapes along with increasingly sustainable methods. The still wine industry is heavily influenced by market trends and customer tastes, which are always changing. Similarly, customers are increasingly searching for unusual and exotic taste profiles, prompting producers to play with various grape varietals and winemaking procedures to suit these demands.
Government rules and policies have an important influence in defining the still wine industry. Regulations governing labeling, promotion, and distribution can have an influence on how manufacturers sell their goods and reach customers. Furthermore, trade agreements and taxes can impact the worldwide flow of still wines, and importers as well as exporters.
The competitive landscape of the still wine market was another important consideration. Established brands, developing wineries, and new entries all help to increase the market's competition. Marketing tactics, branding, and the capacity to respond to changing customer expectations are critical to succeed in this competitive climate.
Environmental sustainability is becoming increasingly essential in the still wine industry. Consumers are growing increasingly aware of the environmental effect of their purchasing decisions, prompting producers to implement sustainable techniques in vineyard administration, winemaking, and packaging. Certifications for organic as well as biodynamic methods of production has become a valuable marketing factor utilized by numerous still wine companies.

















Leave a Comment