Government Initiatives and Funding
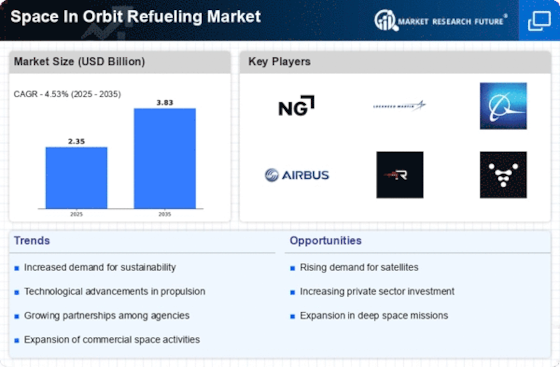
Government initiatives and funding play a crucial role in shaping the Space In Orbit Refueling Market. Various space agencies are increasingly recognizing the strategic importance of in-orbit refueling capabilities for national security and scientific exploration. For instance, investments in space infrastructure and partnerships with private companies are on the rise, with budgets for space exploration reaching unprecedented levels. This financial backing is likely to stimulate innovation and development within the Space In Orbit Refueling Market, fostering a competitive environment that encourages new entrants and technological advancements.
Rising Demand for Satellite Services
The increasing demand for satellite services is a primary driver of the Space In Orbit Refueling Market. As nations and private entities expand their satellite constellations for communication, Earth observation, and scientific research, the need for efficient refueling solutions becomes apparent. The market for satellite services is projected to reach approximately 500 billion USD by 2025, indicating a robust growth trajectory. This surge necessitates innovative refueling technologies to extend satellite lifespans and enhance operational capabilities. Consequently, the Space In Orbit Refueling Market is likely to experience heightened interest from stakeholders aiming to capitalize on this growing demand.
Advancements in Propulsion Technologies
Advancements in propulsion technologies are significantly influencing the Space In Orbit Refueling Market. The development of more efficient propulsion systems, such as electric and hybrid engines, necessitates the availability of in-orbit refueling solutions to maximize their potential. These technologies can reduce launch costs and increase payload capacities, making them attractive to commercial and governmental space missions. As propulsion technology continues to evolve, the Space In Orbit Refueling Market is expected to adapt, providing essential services that support these advanced systems and enhance mission success rates.
Commercial Space Exploration Initiatives
The rise of commercial space exploration initiatives is a significant driver of the Space In Orbit Refueling Market. Private companies are actively pursuing missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond, necessitating reliable refueling options to support long-duration missions. The commercial space sector is projected to grow substantially, with investments reaching billions of dollars in the coming years. This growth creates a demand for in-orbit refueling services that can sustain these ambitious endeavors, thereby propelling the Space In Orbit Refueling Market forward.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Sustainability and environmental considerations are becoming increasingly relevant in the Space In Orbit Refueling Market. As the space sector faces scrutiny regarding its environmental impact, the development of sustainable refueling solutions is gaining traction. This includes the use of green propellants and technologies that minimize space debris. The push for environmentally friendly practices is likely to drive innovation within the Space In Orbit Refueling Market, as companies seek to align with global sustainability goals while maintaining operational efficiency.