Market Analysis
In-depth Analysis of Smart Grid Networking Market Industry Landscape
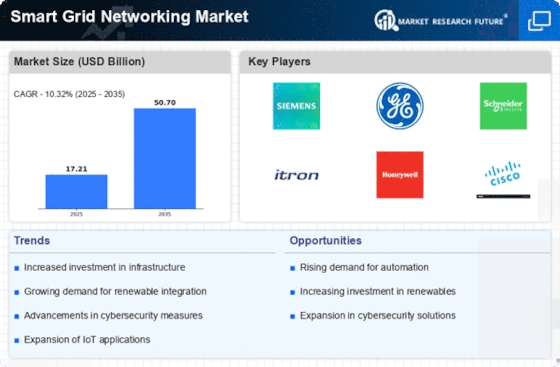
The Smart Grid Networking market is experiencing fast-paced shifts driven by the increasing need for efficient and sustainable energy management. As societies worldwide seek cleaner and more sustainable sources of energy, there has been an increased demand for cutting-edge technologies that can improve the reliability and performance of electrical grids. One of the key drivers shaping the Smart Grid Networking sector is the growing emphasis on grid modernization. Aging infrastructure coupled with the rising risk of cyber security attacks has forced utilities and states to invest in upgrading their electricity grids. Smart grid networking solutions provide a comprehensive approach enabling utilities to monitor, analyze, and manage energy distribution in real-time. This not only enhances the overall efficiency of the grid but also facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into the existing infrastructure. Additionally, the global sustainability drive and reduction of carbon emissions are pushing for the adoption of Smart Grid Networking solutions. These technologies allow utilities to optimize their energy use, reduce transmission losses, and minimize their environmental impact. Furthermore, interoperability and standardization are other significant market factors affecting the Smart Grid Networking sector. Considering that a smart grid ecosystem involves several components and devices, it is imperative to ensure seamless communication and coordination. Standardization efforts are underway to delineate common protocols and linkages that will enable various elements from diverse vendors to operate together closely. This interoperability not only enhances smart grid networks' flexibility but also promotes healthy vendor competition, hence benefiting end-users in terms of cost-effectiveness and innovation. The current context of Smart Grid Networking cannot be more important to the role of cutting-edge communication technologies like 5G and IoT. These advancements make it possible for faster and more reliable information exchange between grid elements, thus facilitating better automation and real-time monitoring. However, some of the significant challenges that hinder the widespread adoption of Smart Grid Networking solutions are high initial costs and difficulties in integrating new technologies into existing grid infrastructure. Overcoming these challenges necessitates joint undertakings by public utilities, state-run services, and technology providers, leading to feasible implementation strategies.

















Leave a Comment