Increased Healthcare Expenditure
The rise in healthcare expenditure across various regions is a notable driver of the Slip Disc Market. As governments and private sectors allocate more resources to healthcare, there is a corresponding increase in funding for spinal health initiatives and treatments. This trend is particularly evident in countries with aging populations, where the demand for effective slip disc treatments is surging. Data indicates that healthcare spending is projected to grow at an annual rate of approximately 7%, which is likely to enhance access to advanced treatment options for patients suffering from slip disc conditions. Furthermore, increased investment in research and development is expected to yield innovative therapies and technologies, thereby expanding the market landscape. As healthcare systems evolve, the focus on improving patient outcomes and reducing the economic burden of spinal disorders will continue to drive growth in the Slip Disc Market.
Advancements in Medical Technology
Technological innovations in medical devices and treatment methodologies are significantly influencing the Slip Disc Market. The introduction of cutting-edge imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, has enhanced diagnostic accuracy, enabling healthcare professionals to identify slip disc conditions more effectively. Furthermore, advancements in surgical techniques, including endoscopic procedures and robotic-assisted surgeries, have improved patient outcomes and reduced recovery times. Data indicates that the market for spinal surgery devices is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of over 5% in the coming years. These technological advancements not only facilitate better treatment options but also foster patient confidence in seeking medical intervention for slip disc issues. As the industry continues to evolve, the integration of artificial intelligence and telemedicine may further transform the landscape, making treatments more accessible and efficient for patients worldwide.
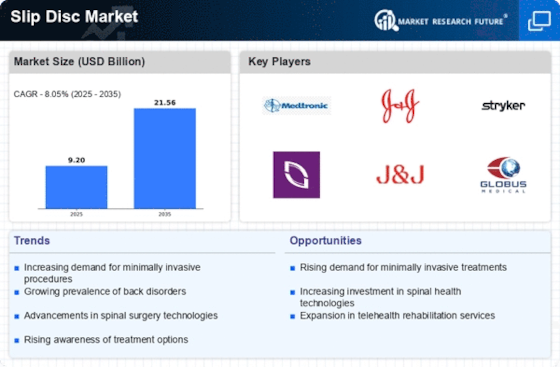
Rising Incidence of Back Disorders
The increasing prevalence of back disorders, particularly among the aging population, appears to be a primary driver of the Slip Disc Market. As individuals age, the risk of developing conditions such as herniated discs escalates, leading to a heightened demand for effective treatment options. According to recent data, approximately 80% of adults experience back pain at some point in their lives, which underscores the urgency for innovative solutions in the Slip Disc Market. This trend is further exacerbated by sedentary lifestyles and poor ergonomics, which contribute to spinal issues. Consequently, healthcare providers are focusing on advanced treatment modalities, including minimally invasive surgeries and rehabilitation programs, to address these challenges. The growing awareness of the importance of spinal health is likely to propel the market forward, as patients seek timely interventions to alleviate pain and improve quality of life.
Growing Demand for Non-Invasive Treatments
The increasing preference for non-invasive treatment options is shaping the dynamics of the Slip Disc Market. Patients are increasingly seeking alternatives to traditional surgical interventions, which often involve longer recovery periods and higher risks. Non-invasive therapies, such as physical therapy, chiropractic care, and acupuncture, are gaining traction as effective methods for managing slip disc symptoms. Market data suggests that the non-invasive segment is expected to witness substantial growth, driven by patient demand for safer and less invasive solutions. Additionally, the rise of telehealth services has made it easier for patients to access these treatments from the comfort of their homes. This shift towards non-invasive approaches not only aligns with patient preferences but also reduces the overall healthcare burden, making it a pivotal factor in the ongoing evolution of the Slip Disc Market.
Rising Awareness and Education on Spinal Health
The growing awareness and education surrounding spinal health are crucial factors influencing the Slip Disc Market. Public health campaigns and educational initiatives aimed at promoting spinal health have led to increased recognition of the importance of early diagnosis and treatment of slip disc conditions. As individuals become more informed about the risks associated with poor spinal health, they are more likely to seek medical advice and intervention. This heightened awareness is reflected in the rising number of consultations and treatments for slip disc issues. Additionally, healthcare providers are increasingly emphasizing preventive measures, such as ergonomic assessments and lifestyle modifications, to mitigate the risk of developing spinal disorders. The ongoing efforts to educate the public about spinal health are likely to foster a proactive approach to treatment, thereby driving demand within the Slip Disc Market.

















Leave a Comment