Market Trends
Key Emerging Trends in the Q Fever Market
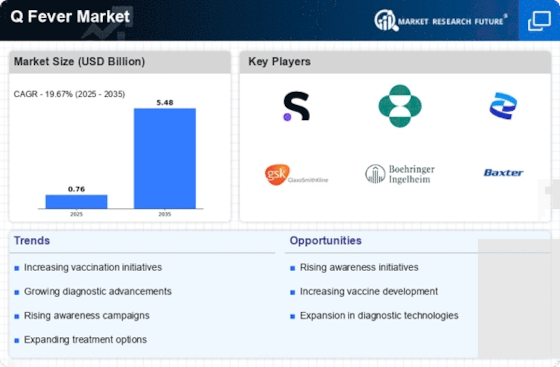
Q Fever is a global zoonotic disease caused by the bacterium Coxiella burnetii. Looking at market trends around Q Fever, it is clear that different factors are shaping diagnostics, treatment and prevention landscapes. In recent times, there has been a pronounced rise in awareness about zoonoses, which puts the Q Fever market on spotlight.
The development of diagnostics has thus propelled the trend in Q Fever markets. Doctors have to resort to more advanced diagnostic techniques as they grapple with an increased understanding of the disease’s intricacy. Serological tests, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays and culture methods play important roles in timely and accurate diagnosis. There is high demand for these diagnostics because quick identification of Q fever enables intervention and management.
Similarly, treatment protocols for Q Fever have shifted significantly illustrating changing market trends. Antibiotics especially doxycycline as well as fluoroquinolones are still used primarily during acute cases. However this is not the case when it comes to chronic forms of the illness where long courses of antibiotics are necessary often accompanied by surgery in some patients. In response to these challenges however, new drugs have been formulated and even combination therapies pursued by the industry players. This shows a dynamic situation regarding R&D efforts aimed at addressing complexities associated with management of Q Fever.
As far as preventing or curbing Q Fever is concerned vaccine development has become a key component within its market standing alongside public health strategies too because they are very necessary herein too when one looks at them from this perspective Vaccine development to reduce morbidity and mortality due to Q fever is considered significant hence effective ones must be developed and widely adopted across all economies Accordingly ongoing research has brought about positive developments that would assist in combating this zoonotic disease through vaccination technology campaigns aiming at sensitizing people about how q fever spreads plus prevention options so far done globally have considerably influenced marketplace dynamics.
Geographically, market trends in Q Fever vary due to factors such as climate, agricultural practices and veterinary policies. In regions where livestock are more prevalent, which also have increased interrelationship between animals and humans; there is a higher incidence of Q Fever. As such, these markets are characterized by an increased focus on diagnostics, treatment and preventive measures. Conversely, areas with a low prevalence may concentrate on preparedness for outbreaks or conducting awareness campaigns.
Technology is also driving market trends for Q Fever as it intersects with the healthcare sector. Telemedicine and digital health platforms allow remote consultations to be done hence timely diagnosis and treatment recommendations can be made. Additionally, digital platforms are being used as tools through which information about Q fever is being disseminated globally raising awareness among medical practitioners.

















Leave a Comment