Market Analysis
In-depth Analysis of Precision Farming Market Industry Landscape
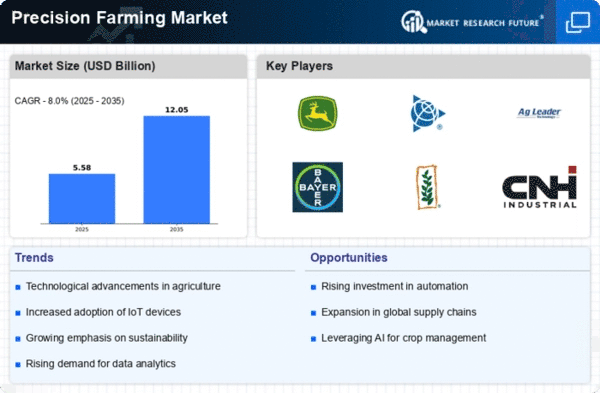
IT also serves a major function in the market dynamics of precision farming. The use of data-based technologies such as sensors, GPS technology and drones allows farmers to monitor their fields in real time. This information allows them to make rational judgments about irrigation, fertilizers and pesticides. The efficiency of production increase as their resource utilization becomes more optimal. By doing this, farmers can cut input costs and reduce environmental impact while enhancing crop yield. Precision farming is also reshaping the competitive structure of agriculture. The proportion of producers using such methods has been steadily increasing. These technologies hold the promise of huge savings and higher production, with large-scale farming operations and agribusinesses now leading the way in their adoption. However, small and middle farms have also found the benefits of precision farming. These governments provide incentives and subsidies to encourage agriculture-related use. Another consideration is how climatic changes and their effect on agriculture affect the market forces for precision farming. Uncertain rainfall, extreme temperatures and manifestly unruly weather conditions make the work very hard for farmers. Adaptive response is possible through precision farming technologies. Farmers can observe their own approaches and change to suit changing environmental circumstances. In particular, this adaptability reduces the threats of climate change; at the same time it further strengthens agricultural sustainability over very long periods. Collaboration is bringing technology providers and agricultural equipment manufacturers closer, making precision farming increasingly prevalent. Such collaborations create integrated solutions which combine hardware, software and data into a complete whole. The aim is to build complete precision farm systems that fit everyone, big or small. Government policy and the regulatory framework are also factors influencing precision farming. Food security, environmental concern and economic sustainability: Many countries recognize precision farming with increasing frequency. Therefore, many governments are formulating policies encouraging the use of precision farming technologies. Examples include subsidies and financial incentives, along with educational programs. The level of consumer awareness and preference also has an effect on market dynamics for precision farming. Today's consumers are demanding sustainable and ethically produced food products. They're more cognizant of what agricultural practices are associated with the food they eat.
















Leave a Comment