Top Industry Leaders in the Next Generation Computing Market

Competitive Landscape of Next Generation Computing Market
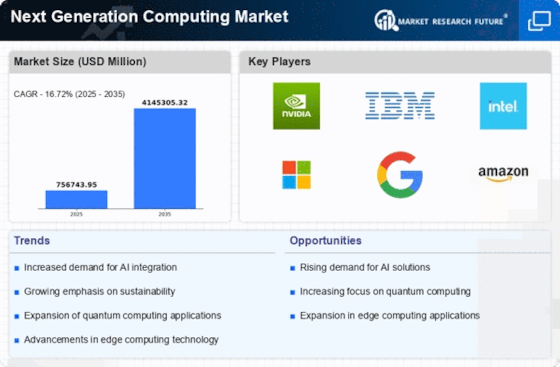
The next generation computing (NGC) market pulsates with innovation, promising to revolutionize how we process and utilize information. This landscape, encompassing technologies like quantum computing, neuromorphic computing, and advanced AI, is attracting major players and nimble startups alike, all vying for a piece of the projected multi-billion dollar pie.
Key Players:
- IBM Corporation
- Alphabet Inc
- Amazon Web Services, Inc.
- Microsoft
- Advanced Micro Devices, Inc
- Atos SE
- Intel Corporation
- NVIDIA Corporation
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Dell Inc.
- Alibaba Group Holding Limited
- Oracle Corporation
- NEC Corporation
Strategies Adopted by Key Players:
- Established Tech Giants: IBM, Microsoft, Google, and Intel hold a significant advantage due to their R&D prowess, hardware dominance, and existing cloud infrastructure. They're pursuing diverse strategies, from building their own quantum and neuromorphic hardware to investing in startups and offering cloud-based access to these technologies.
- Quantum Computing Startups: D-Wave, IonQ, and Rigetti are leading the charge with their specialized quantum hardware. Their strategies focus on developing user-friendly interfaces, building partnerships with research institutions and enterprises, and demonstrating tangible applications in drug discovery, materials science, and financial modeling.
- Neuromorphic Computing Players: Intel's Loihi and Cerebras' CS-1 are frontrunners in this space. Their strategies revolve around creating neuromorphic chips that mimic the human brain's architecture, attracting customers with their potential for efficient processing of complex data sets in fields like autonomous driving and image recognition.
- AI Software Companies: Google's TensorFlow and DeepMind, along with Microsoft's Azure AI, are leveraging their existing AI expertise to develop software tools and frameworks compatible with NGC hardware. Their focus is on making these technologies accessible and user-friendly for a broader range of developers and businesses.
Factors for Market Share Analysis:
- Technology Maturity: Companies with more advanced and commercially viable hardware solutions will hold an edge.
- Industry Focus: The ability to demonstrate clear applications in specific sectors like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing will attract customers and investors.
- Partnerships and Ecosystem Building: Collaborations with research institutions, cloud providers, and enterprise customers will be crucial for wider adoption and market penetration.
- Talent Acquisition: Attracting and retaining top engineers and scientists with expertise in these emerging fields will be a key differentiator.
New and Emerging Companies:
- Quantum Startup Landscape: Xanadu, PsiQuantum, and QuTech are among the rising stars, exploring alternative approaches to quantum computing like photonic and topological qubits.
- Neuromorphic Chips on the Rise: Brainchip and Mythic are developing neuromorphic chips targeting specific applications like edge computing and robotics.
- Open-Source Software Players: NumPy and PyTorch are building open-source frameworks for developing and deploying AI applications on NGC hardware, fostering wider community participation and innovation.
Current Company Investment Trends:
- M&A and Partnerships: Strategic acquisitions and partnerships are increasing, with established players like Microsoft acquiring quantum startups like QuantumWare and Rigetti, and NVIDIA collaborating with Cerebras on AI workloads.
- Venture Capital Injection: VC funding for NGC startups is on the rise, with companies like PsiQuantum and Xanadu securing significant investments.
- Focus on Cloud-based Access: Major cloud providers like Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure are offering cloud-based access to NGC hardware, lowering barriers to entry for smaller businesses and researchers.
Latest Company Updates:
The new platform, which comes in a variety of configurations, is designed to tackle the most intricate generative AI workloads in the world, including recommender systems, vector databases, and big language models.
The 12-qubit quantum-dot silicon chip was introduced by semiconductor behemoth Intel in 2023, marking a significant step towards the eventual mass production of quantum computers. Compared to traditional computers, quantum computers are far more powerful devices that can tackle very complicated computational tasks considerably more quickly.
Beta feature