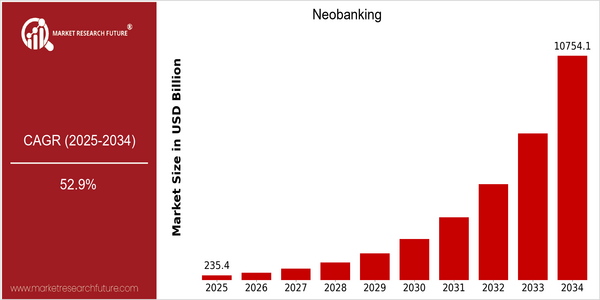
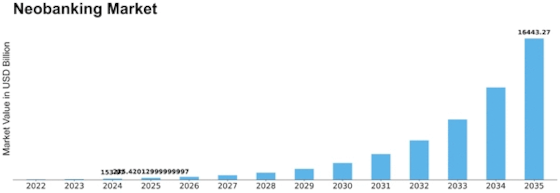
Neobanking Size
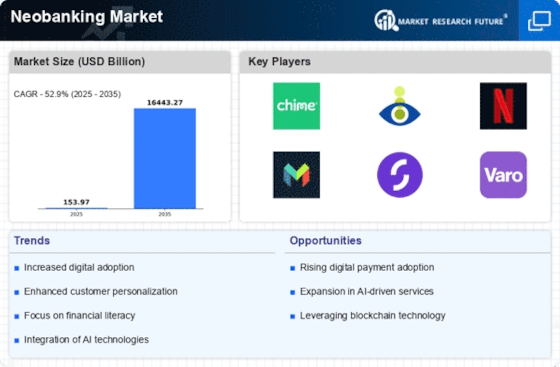
Market Size Snapshot
| Year | Value |
|---|---|
| 2025 | USD 235.43 Billion |
| 2034 | USD 10754.12 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 52.9 % |
Note – Market size depicts the revenue generated over the financial year
The Neobanking industry is expected to experience tremendous growth. The current market capitalization of $ 235,431,000,000 is projected to reach $ 10,754,112,000 by 2034. This remarkable increase corresponds to a CAGR of 52.9% over a nine-year period, indicating a strong and increasing demand for digital banking services. This growth can be attributed to a number of factors, including the increasing penetration of mobile devices, the advancement of financial technology and the growing demand for a simple, intuitive and easy-to-use banking experience. As the traditional banking system evolves, Neobanks are seizing the opportunity to offer new and improved services, adapted to the needs of the technologically advanced customer. Artificial intelligence, machine learning and the blockchain are driving the Neobanking revolution, enabling improved customer service, a greater variety of financial products and improved security. A number of Neobanks, including Chime, Revolut and N26, are investing heavily in new products and technology to capture market share. Their efforts not only help them compete, but also contribute to the growth of the Neobanking industry, as they strive to meet the evolving needs of consumers in an increasingly digital financial environment.
Regional Market Size
Regional Deep Dive
The neobanking market is experiencing a strong growth in various regions of the world, driven by technological advances, changing consumer preferences, and a growing demand for digital financial services. In North America, the market is characterized by a high degree of innovation and competition, with financial institutions increasingly collaborating with fintechs. Europe is characterized by a variety of regulatory frameworks. The Asia-Pacific region is experiencing a rapid uptake of digital banking solutions, primarily driven by the large number of unbanked. In the Middle East and Africa, the neobanking market is experiencing strong growth, supported by government initiatives aimed at promoting financial inclusion. Latin America is also emerging as a major market, with the number of neobanks growing rapidly.
Europe
- The European Union's PSD2 regulation is driving open banking initiatives, allowing neobanks like N26 and Revolut to access customer data from traditional banks, thereby enhancing their service offerings.
- Sustainability is becoming a focal point for neobanks in Europe, with companies like Tomorrow Bank promoting eco-friendly banking practices, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Asia Pacific
- Countries like India and China are witnessing a boom in neobanking, with platforms such as Paytm and WeBank leveraging mobile technology to reach millions of unbanked individuals.
- Government initiatives, such as the Digital India program, are supporting the growth of neobanks by promoting digital literacy and financial inclusion, creating a favorable environment for fintech innovation.
Latin America
- Neobanks like Nubank in Brazil are revolutionizing the banking sector by offering no-fee services and user-friendly mobile applications, attracting millions of customers.
- The region's high smartphone penetration and increasing internet access are driving the adoption of neobanking, with many consumers preferring digital solutions over traditional banking.
North America
- The rise of embedded finance is transforming the neobanking landscape, with companies like Chime and Varo Money integrating banking services into various platforms, enhancing user experience and accessibility.
- Regulatory changes, such as the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency's (OCC) charter for fintech banks, are paving the way for more neobanks to operate legally, fostering competition and innovation in the financial sector.
Middle East And Africa
- The UAE is emerging as a hub for neobanking, with startups like Liv. and YAP gaining traction by offering tailored financial solutions to tech-savvy consumers.
- Regulatory bodies in the region are increasingly supportive of fintech, with the Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM) launching a regulatory framework for digital banks, encouraging investment and innovation.
Did You Know?
“As of 2023, over 50% of neobank users in Europe are under the age of 35, highlighting the appeal of digital banking among younger consumers.” — European Banking Authority
Segmental Market Size
The neobanking sector is growing fast, driven by the growing demand for digital financial services from technology-savvy consumers. The demand is based on the desire for cashless transactions, the need for a personalised banking experience and the emergence of fintech innovations that enhance customer engagement. Open banking initiatives, such as the one launched in Europe, are a major driver of competition and innovation. At present, neobanking is in the implementation stage, with notable players such as Chime in the United States and Revolut in Europe leading the way. These companies are a good example of how neobanks are using technology to provide seamless banking experiences. Applications include mobile banking, peer-to-peer payments and budgeting tools, which meet consumers’ changing needs. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the shift to digital banking, as users seek contactless solutions. Artificial intelligence and the blockchain are also shaping the sector, improving security and operational efficiency.
Future Outlook
From 2025 to 2034, the market for neobanks is expected to grow at an astonishing rate of 52% a year. This spectacular growth is driven by the growing use of digital financial services, especially among young people who are looking for the most convenient and accessible solutions. In 2034, it is expected that neobanks will take over more than 30% of the world banking market, thereby significantly increasing their penetration in both developed and developing economies. The neobanking industry will be greatly influenced by the technological progress of artificial intelligence, machine learning and blockchain. These new developments will not only make it easier to provide banking services and improve customer experiences, but also increase security, thereby addressing the concerns of consumers about data privacy and fraud. Also, the regulatory framework for digital financial innovations is gradually developing and many governments are aware of the need for financial services for the unbanked. It is expected that neobanks will continue to develop and expand their services, including more personalised financial products and integrated services, thereby redefining the banking experience, making it more customer-friendly and efficient.

















Leave a Comment