-
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
-
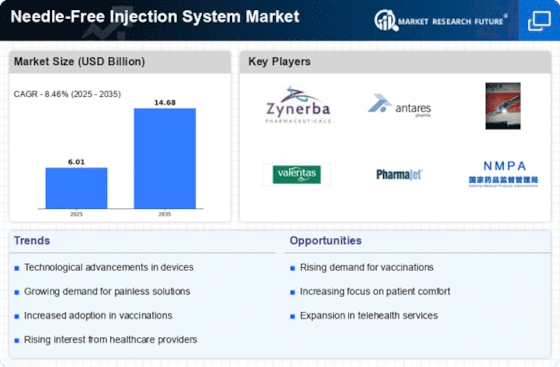
Market Overview
-
Key Findings
-
Market Segmentation
-
Competitive Landscape
-
Challenges and Opportunities
-
Future Outlook
-
MARKET INTRODUCTION
-
Definition
-
Scope of the study
-
Research Objective
-
Assumption
-
Limitations
-
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
-
Overview
-
Data Mining
-
Secondary Research
-
Primary Research
-
Primary Interviews and Information Gathering Process
-
Breakdown of Primary Respondents
-
Forecasting Model
-
Market Size Estimation
-
Bottom-Up Approach
-
Top-Down Approach
-
Data Triangulation
-
Validation
-
MARKET DYNAMICS
-
Overview
-
Drivers
-
Restraints
-
Opportunities
-
MARKET FACTOR ANALYSIS
-
Value chain Analysis
-
Porter's Five Forces Analysis
-
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
-
Bargaining Power of Buyers
-
Threat of New Entrants
-
Threat of Substitutes
-
Intensity of Rivalry
-
COVID-19 Impact Analysis
-
Market Impact Analysis
-
Regional Impact
-
Opportunity and Threat Analysis
-
Needle-Free Injection System Market, BY Application (USD Billion)
-
Vaccination
-
Insulin Delivery
-
Pain Management
-
Hormone Replacement Therapy
-
Needle-Free Injection System Market, BY Technology (USD Billion)
-
Gas-Propelled Technology
-
Spring-Loaded Technology
-
Vibration-Enabled Technology
-
Needle-Free Injection System Market, BY End Use (USD Billion)
-
Hospitals
-
Clinics
-
Home Care Settings
-
Research Laboratories
-
Needle-Free Injection System Market, BY Distribution Channel (USD Billion)
-
Direct Sales
-
Distributors
-
Online Sales
-
Needle-Free Injection System Market, BY Regional (USD Billion)
-
North America
-
US
-
Canada
-
Europe
-
Germany
-
UK
-
France
-
Russia
-
Italy
-
Spain
-
Rest of Europe
-
APAC
-
China
-
India
-
Japan
-
South Korea
-
Malaysia
-
Thailand
-
Indonesia
-
Rest of APAC
-
South America
-
Brazil
-
Mexico
-
Argentina
-
Rest of South America
-
MEA
-
GCC Countries
-
South Africa
-
Rest of MEA
-
Competitive Landscape
-
Overview
-
Competitive Analysis
-
Market share Analysis
-
Major Growth Strategy in the Needle-Free Injection System Market
-
Competitive Benchmarking
-
Leading Players in Terms of Number of Developments in the Needle-Free Injection System Market
-
Key developments and growth strategies
-
New Product Launch/Service Deployment
-
Merger & Acquisitions
-
Joint Ventures
-
Major Players Financial Matrix
-
Sales and Operating Income
-
Major Players R&D Expenditure. 2023
-
Company Profiles
-
Antares Pharma
-
Financial Overview
-
Products Offered
-
Key Developments
-
SWOT Analysis
-
Key Strategies
-
Injex Pharma
-
Financial Overview
-
Products Offered
-
Key Developments
-
SWOT Analysis
-
Key Strategies
-
Vaxess Technologies
-
Financial Overview
-
Products Offered
-
Key Developments
-
SWOT Analysis
-
Key Strategies
-
InsuJet
-
Financial Overview
-
Products Offered
-
Key Developments
-
SWOT Analysis
-
Key Strategies
-
Zyler Medical
-
Financial Overview
-
Products Offered
-
Key Developments
-
SWOT Analysis
-
Key Strategies
-
Euroinject
-
Financial Overview
-
Products Offered
-
Key Developments
-
SWOT Analysis
-
Key Strategies
-
Janssen Pharmaceuticals
-
Financial Overview
-
Products Offered
-
Key Developments
-
SWOT Analysis
-
Key Strategies
-
Medimop Medical Projects
-
Financial Overview
-
Products Offered
-
Key Developments
-
SWOT Analysis
-
Key Strategies
-
PharmaJet
-
Financial Overview
-
Products Offered
-
Key Developments
-
SWOT Analysis
-
Key Strategies
-
Sandoz
-
Financial Overview
-
Products Offered
-
Key Developments
-
SWOT Analysis
-
Key Strategies
-
Syringe Technology Corporation
-
Financial Overview
-
Products Offered
-
Key Developments
-
SWOT Analysis
-
Key Strategies
-
Vaccine Technologies
-
Financial Overview
-
Products Offered
-
Key Developments
-
SWOT Analysis
-
Key Strategies
-
Valeritas Holdings
-
Financial Overview
-
Products Offered
-
Key Developments
-
SWOT Analysis
-
Key Strategies
-
Dune Medical Devices
-
Financial Overview
-
Products Offered
-
Key Developments
-
SWOT Analysis
-
Key Strategies
-
National Medical Products
-
Financial Overview
-
Products Offered
-
Key Developments
-
SWOT Analysis
-
Key Strategies
-
Appendix
-
References
-
Related Reports
-
LIST Of tables
-
LIST OF ASSUMPTIONS
-
North America Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
North America Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
North America Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
North America Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
North America Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
US Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
US Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
US Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
US Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
US Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Canada Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Canada Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Canada Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Canada Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Canada Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Europe Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Europe Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Europe Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Europe Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Europe Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Germany Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Germany Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Germany Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Germany Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Germany Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
UK Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
UK Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
UK Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
UK Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
UK Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
France Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
France Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
France Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
France Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
France Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Russia Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Russia Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Russia Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Russia Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Russia Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Italy Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Italy Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Italy Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Italy Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Italy Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Spain Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Spain Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Spain Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Spain Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Spain Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of Europe Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of Europe Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of Europe Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of Europe Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of Europe Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
APAC Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
APAC Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
APAC Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
APAC Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
APAC Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
China Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
China Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
China Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
China Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
China Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
India Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
India Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
India Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
India Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
India Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Japan Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Japan Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Japan Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Japan Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Japan Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
South Korea Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
South Korea Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
South Korea Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
South Korea Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
South Korea Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Malaysia Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Malaysia Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Malaysia Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Malaysia Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Malaysia Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Thailand Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Thailand Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Thailand Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Thailand Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Thailand Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Indonesia Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Indonesia Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Indonesia Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Indonesia Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Indonesia Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of APAC Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of APAC Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of APAC Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of APAC Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of APAC Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
South America Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
South America Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
South America Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
South America Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
South America Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Brazil Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Brazil Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Brazil Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Brazil Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Brazil Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Mexico Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Mexico Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Mexico Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Mexico Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Mexico Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Argentina Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Argentina Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Argentina Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Argentina Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Argentina Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of South America Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of South America Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of South America Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of South America Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of South America Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
MEA Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
MEA Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
MEA Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
MEA Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
MEA Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
GCC Countries Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
GCC Countries Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
GCC Countries Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
GCC Countries Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
GCC Countries Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
South Africa Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
South Africa Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
South Africa Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
South Africa Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
South Africa Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of MEA Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY APPLICATION, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of MEA Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of MEA Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY END USE, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of MEA Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
Rest of MEA Needle-Free Injection System Market SIZE ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGIONAL, 2019-2032 (USD Billions)
-
PRODUCT LAUNCH/PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT/APPROVAL
-
ACQUISITION/PARTNERSHIP
-
LIST Of figures
-
MARKET SYNOPSIS
-
NORTH AMERICA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS
-
US NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
US NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
US NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
US NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
US NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
CANADA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
CANADA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
CANADA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
CANADA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
CANADA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
EUROPE NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS
-
GERMANY NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
GERMANY NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
GERMANY NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
GERMANY NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
GERMANY NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
UK NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
UK NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
UK NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
UK NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
UK NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
FRANCE NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
FRANCE NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
FRANCE NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
FRANCE NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
FRANCE NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
RUSSIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
RUSSIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
RUSSIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
RUSSIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
RUSSIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
ITALY NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
ITALY NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
ITALY NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
ITALY NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
ITALY NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
SPAIN NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
SPAIN NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
SPAIN NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
SPAIN NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
SPAIN NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
REST OF EUROPE NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
REST OF EUROPE NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
REST OF EUROPE NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
REST OF EUROPE NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
REST OF EUROPE NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
APAC NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS
-
CHINA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
CHINA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
CHINA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
CHINA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
CHINA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
INDIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
INDIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
INDIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
INDIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
INDIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
JAPAN NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
JAPAN NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
JAPAN NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
JAPAN NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
JAPAN NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
SOUTH KOREA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
SOUTH KOREA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
SOUTH KOREA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
SOUTH KOREA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
SOUTH KOREA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
MALAYSIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
MALAYSIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
MALAYSIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
MALAYSIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
MALAYSIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
THAILAND NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
THAILAND NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
THAILAND NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
THAILAND NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
THAILAND NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
INDONESIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
INDONESIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
INDONESIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
INDONESIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
INDONESIA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
REST OF APAC NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
REST OF APAC NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
REST OF APAC NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
REST OF APAC NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
REST OF APAC NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
SOUTH AMERICA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS
-
BRAZIL NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
BRAZIL NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
BRAZIL NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
BRAZIL NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
BRAZIL NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
MEXICO NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
MEXICO NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
MEXICO NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
MEXICO NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
MEXICO NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
ARGENTINA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
ARGENTINA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
ARGENTINA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
ARGENTINA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
ARGENTINA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
REST OF SOUTH AMERICA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
REST OF SOUTH AMERICA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
REST OF SOUTH AMERICA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
REST OF SOUTH AMERICA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
REST OF SOUTH AMERICA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
MEA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS
-
GCC COUNTRIES NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
GCC COUNTRIES NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
GCC COUNTRIES NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
GCC COUNTRIES NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
GCC COUNTRIES NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
SOUTH AFRICA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
SOUTH AFRICA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
SOUTH AFRICA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
SOUTH AFRICA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
SOUTH AFRICA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
REST OF MEA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY APPLICATION
-
REST OF MEA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY TECHNOLOGY
-
REST OF MEA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY END USE
-
REST OF MEA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
-
REST OF MEA NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET ANALYSIS BY REGIONAL
-
KEY BUYING CRITERIA OF NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET
-
RESEARCH PROCESS OF MRFR
-
DRO ANALYSIS OF NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET
-
DRIVERS IMPACT ANALYSIS: NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET
-
RESTRAINTS IMPACT ANALYSIS: NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET
-
SUPPLY / VALUE CHAIN: NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET
-
NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET, BY APPLICATION, 2024 (% SHARE)
-
NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET, BY APPLICATION, 2019 TO 2032 (USD Billions)
-
NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2024 (% SHARE)
-
NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2019 TO 2032 (USD Billions)
-
NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET, BY END USE, 2024 (% SHARE)
-
NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET, BY END USE, 2019 TO 2032 (USD Billions)
-
NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2024 (% SHARE)
-
NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET, BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL, 2019 TO 2032 (USD Billions)
-
NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET, BY REGIONAL, 2024 (% SHARE)
-
NEEDLE-FREE INJECTION SYSTEM MARKET, BY REGIONAL, 2019 TO 2032 (USD Billions)
-
BENCHMARKING OF MAJOR COMPETITORS

















Leave a Comment