Rising Energy Costs
In Japan, the increasing cost of conventional energy sources has prompted a shift towards alternative energy solutions, including the small wind-power market. As fossil fuel prices fluctuate, consumers and businesses are seeking more stable and sustainable energy options. The average electricity price in Japan has seen a steady rise, with residential rates reaching approximately 27.5 JPY/kWh in 2025. This trend makes small wind systems an attractive investment, as they can provide a degree of energy independence and cost savings over time. The potential for reduced energy bills and the ability to generate electricity on-site are compelling factors driving the adoption of small wind technology in both urban and rural areas.
Government Incentives and Subsidies
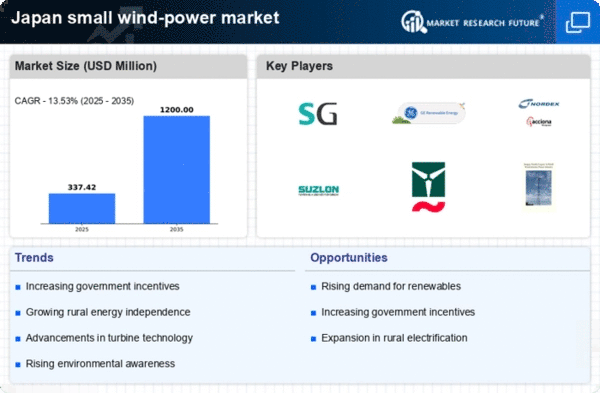
The small wind-power market in Japan benefits from various government incentives and subsidies aimed at promoting renewable energy sources. The Japanese government has implemented policies that provide financial support for small wind installations, which can cover a significant portion of the initial investment costs. For instance, the Feed-in Tariff (FiT) program guarantees a fixed payment for electricity generated from renewable sources, including small wind systems. This financial backing encourages homeowners and businesses to invest in small wind technology, thereby stimulating market growth. As of 2025, the government aims to increase the share of renewable energy in the national energy mix to 36-38% by 2030, which further underscores the importance of the small wind-power market in achieving these targets.
Increased Demand for Energy Independence
The small wind-power market in Japan is witnessing a growing demand for energy independence among consumers and businesses. As energy security becomes a priority, many are looking for ways to reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels. Small wind systems offer a viable solution, allowing users to generate their own electricity and mitigate the risks associated with energy supply disruptions. This trend is particularly pronounced in rural areas, where access to the grid may be limited. By investing in small wind technology, individuals and communities can enhance their energy resilience and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
Technological Innovations in Wind Turbines
The small wind-power market in Japan is experiencing a wave of technological innovations that enhance the efficiency and reliability of wind turbines. Advances in materials science and aerodynamics have led to the development of smaller, more efficient turbines that can operate effectively in low-wind conditions, which is particularly beneficial for Japan's diverse geographical landscape. For example, new turbine designs are capable of generating power at wind speeds as low as 3 m/s, expanding the potential for small wind installations in various locations. These innovations not only improve energy output but also reduce maintenance costs, making small wind systems more appealing to consumers and businesses alike.
Environmental Regulations and Sustainability Goals
Japan's commitment to environmental sustainability is driving the small wind-power market forward. The government has set ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, aiming for a 26% reduction from 2013 levels by 2030. This regulatory framework encourages the adoption of renewable energy sources, including small wind systems, as part of a broader strategy to combat climate change. Additionally, local governments are implementing stricter environmental regulations that promote the use of clean energy technologies. As businesses and individuals seek to comply with these regulations, the small wind-power market is likely to see increased investment and growth, aligning with Japan's sustainability goals.