Regulatory Incentives and Support
The Hydrogen-Cooled Synchronous Condenser Market benefits from a favorable regulatory environment that encourages the adoption of cleaner technologies. Governments worldwide are implementing policies and incentives aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting energy efficiency. These regulations often include financial incentives for utilities that invest in hydrogen-cooled synchronous condensers, as they contribute to grid stability and support the integration of renewable energy sources. The presence of such supportive frameworks is likely to enhance market growth, as utilities seek to comply with regulations while also improving their operational efficiency. This regulatory backing is crucial for fostering innovation and investment in the hydrogen-cooled synchronous condenser sector.
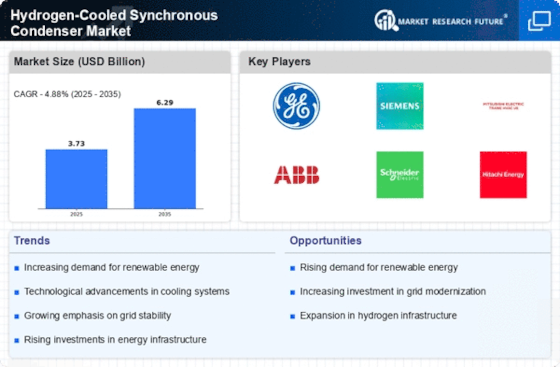
Increasing Demand for Renewable Energy
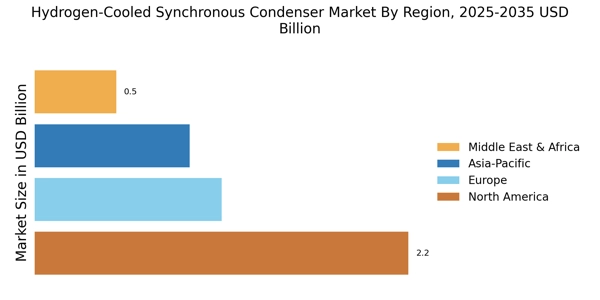
The Hydrogen-Cooled Synchronous Condenser Market is experiencing a surge in demand due to the global shift towards renewable energy sources. As countries strive to meet their carbon reduction targets, the integration of renewable energy into existing power grids becomes essential. Hydrogen-cooled synchronous condensers play a pivotal role in stabilizing these grids, particularly in accommodating the intermittent nature of renewable sources like wind and solar. The market for these condensers is projected to grow significantly, with estimates suggesting a compound annual growth rate of over 6% in the coming years. This growth is driven by the need for reliable power quality and grid stability, which hydrogen-cooled synchronous condensers can effectively provide.
Growing Focus on Energy Storage Solutions
The Hydrogen-Cooled Synchronous Condenser Market is increasingly intertwined with the growing emphasis on energy storage solutions. As energy storage becomes a critical component of modern power systems, hydrogen-cooled synchronous condensers are recognized for their ability to provide reactive power support and enhance grid reliability. The need for effective energy storage solutions is underscored by the rising penetration of renewable energy sources, which necessitate robust systems to manage fluctuations in supply and demand. Market analysts indicate that the energy storage sector is expected to witness substantial growth, which in turn will likely drive the demand for hydrogen-cooled synchronous condensers as essential components of these systems.
Technological Innovations in Power Systems
Technological advancements within the Hydrogen-Cooled Synchronous Condenser Market are propelling the adoption of these systems. Innovations such as enhanced cooling techniques and improved efficiency metrics are making hydrogen-cooled condensers more attractive to utility companies. These advancements not only reduce operational costs but also extend the lifespan of the equipment. Furthermore, the integration of smart grid technologies is enabling better monitoring and control of power systems, which is crucial for maintaining grid stability. As utilities increasingly invest in modernizing their infrastructure, the demand for advanced hydrogen-cooled synchronous condensers is likely to rise, reflecting a broader trend towards smarter, more efficient energy systems.
Rising Investment in Infrastructure Development
Investment in infrastructure development is a key driver for the Hydrogen-Cooled Synchronous Condenser Market. As nations prioritize the modernization of their energy infrastructure, there is a growing recognition of the importance of reliable power systems. Hydrogen-cooled synchronous condensers are increasingly being deployed in new projects aimed at enhancing grid stability and efficiency. This trend is particularly evident in regions where aging infrastructure is being upgraded to accommodate new energy demands. The market is projected to benefit from these investments, with forecasts suggesting a significant increase in the deployment of hydrogen-cooled synchronous condensers in the coming years, as utilities seek to enhance their operational capabilities.