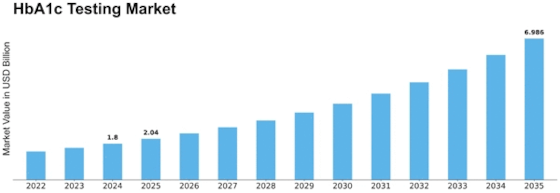
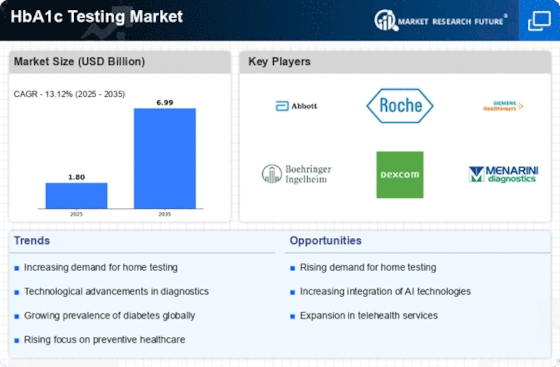
Hba1c Testing Size
HbA1c Testing Market Growth Projections and Opportunities
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is a variant of hemoglobin that becomes bound to glucose in the bloodstream. This specific type of hemoglobin serves as the focus of the HbA1c test, offering patients insights into their average blood sugar levels over a span of 2 to 3 months. The test is alternatively referred to as the glycated hemoglobin test or glycohemoglobin test. Understanding HbA1c levels is crucial in managing diabetes. The normal range for HbA1c is considered to be less than 6%. This percentage represents the proportion of hemoglobin that has bonded with glucose during the testing period. In essence, a lower HbA1c value indicates better blood sugar control within the specified timeframe. When HbA1c levels surpass the normal range and rise above 6%, it signals potential challenges in diabetes management. Elevated HbA1c levels are indicative of inadequate control over blood sugar levels. This means that over the past 2 to 3 months, blood sugar levels have been consistently higher than what is considered optimal for diabetes management. Monitoring HbA1c levels is thus a critical aspect of diabetes care, providing a more comprehensive and extended perspective on glycemic control compared to regular blood sugar tests.
The HbA1c test is particularly beneficial because it reflects the average blood sugar concentration over a more extended period, offering a more stable and reliable indicator of diabetes management. This is in contrast to daily blood sugar tests, which provide momentary snapshots and may not capture the overall trend. As a result, healthcare professionals commonly use the HbA1c test to assess the effectiveness of diabetes treatment plans and to make informed adjustments as needed. In summary, HbA1c is a significant marker in diabetes management, offering a retrospective view of blood sugar control over the past 2 to 3 months. Maintaining HbA1c levels within the normal range is essential for effective diabetes care, as it reflects optimal blood sugar control and reduces the risk of complications associated with poorly managed diabetes. Regular monitoring through the HbA1c test enables individuals and healthcare providers to make informed decisions to enhance diabetes management and overall well-being.

















Leave a Comment