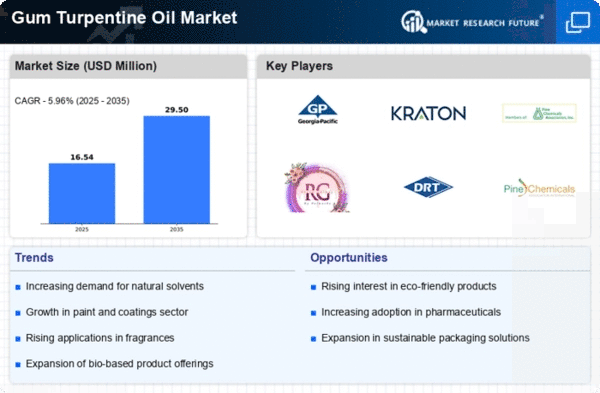
Market Analysis
In-depth Analysis of Gum Turpentine Oil Market Industry Landscape
The pine chemical industry's resilience can be attributed to its foundation on sustainable practices, practices that have proven effective over many centuries. Even before the term "sustainable development" became widely known, this industry was already championing sustainability. The tradition of harvesting compounds from pine trees can be traced back to ancient times, even mentioned in the Bible. In the modern era, the industry places great importance on responsible forest management, efficient extraction of raw materials, and sustainable operations to ensure the long-term value of this natural resource.
There are three primary methods employed to extract compounds from pine trees. During the pulping process, Crude Tall Oil (CTO) and Crude Sulphate Turpentine (CST) are recovered as co-products. These chemicals, naturally present in pine trees, play a vital role in the papermaking process. Another method involves extracting "oleoresin" by tapping into pine trees, which can then be separated into Gum Rosin (GR) and Gum Turpentine. Additionally, old pine tree stumps are ground up and undergo solvent extraction to produce wood rosin and specific terpenes, although this constitutes a niche industry.
These extracted compounds serve as the chemical building blocks for a wide range of finished goods. Any residues left after extraction are burned to generate steam for bio-refinery processes when further upgrading is not feasible. Pine trees are strategically utilized for their sap for a brief period before being cut down and processed into timber or chips for pulp. Even the parts of the tree that are not directly used are converted into fuel. After harvesting, new trees are planted, ensuring a continuous and sustainable cycle of production for the future.
With the increasing global preference for eco-friendly products, there has been a corresponding surge in demand for chemicals derived from pine. These chemicals play a crucial role in reducing the carbon footprint, utilizing renewable and naturally occurring resources to create essential products. The raw materials for pine-derived compounds come from various sources in the forestry sector, including living trees, pine stumps, and logs.
The American Chemistry Council (ACC) foresees rapid growth in the market between 2022 and 2030 due to the rising popularity of pine-derived compounds compared to their synthetic counterparts. This shift in consumer preference, coupled with the continued demand for rosin and TOFA (Tall Oil Fatty Acid) across diverse industries, is expected to fuel significant growth during the forecast period.
In simpler terms, the pine chemical industry has a long history of sustainable practices, even before sustainability became a trend. They've been extracting useful compounds from pine trees for centuries, and today, they focus on responsible forest management and sustainable operations. Different methods are used to extract chemicals from pine trees, and these chemicals are used to make a wide variety of products. The leftover bits are even used to generate steam for various processes. Pine trees are used smartly – their sap is collected for a while, and then they are cut down for timber and other uses. The unused parts become fuel, and new trees are planted for future use. As people become more interested in eco-friendly products, the demand for chemicals from pine trees is growing. These chemicals are considered more environmentally friendly as they use renewable resources. According to the American Chemistry Council, the market for these pine-derived compounds is expected to grow rapidly due to increased popularity and demand.

















Leave a Comment