Market Trends
Key Emerging Trends in the Farming as a Service Market
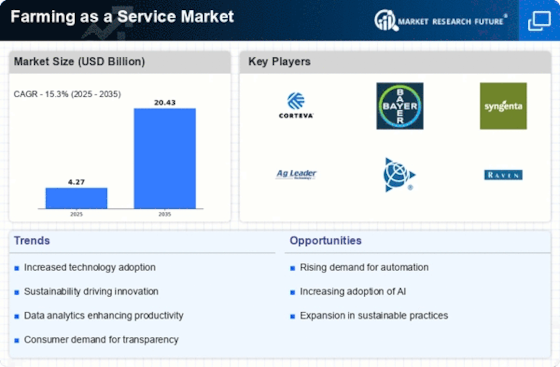
The Farming as a Service (FaaS) market is transforming traditional agriculture, offering innovative solutions to enhance efficiency and sustainability. Market share positioning within the FaaS sector involves a multifaceted approach, with technological innovation at its core. Companies invest in research and development to introduce cutting-edge technologies, such as precision farming, IoT (Internet of Things), and data analytics, into their service offerings. These technologies make the farmers more responsive to the environment, whereas through the use of real-time insights farmers may take actions like increasing the efficiency of crop yields, and reducing the use of resources and make decisions based on data
Strategic agreements and collaborations play a decisive role in Future Farming as a Service industry by helping to outline market share. The mission of FaaS suppliers is an acquisition of partnerships with agricultural equipment manufacturers, innovators, and agrotech startups for a comprehensive and all-embracing solution. These partnerships achieve not only the large customer base of FaaS but also publicize the coherent ecology. Collective works lead to a tendency that each practitioner comes up with useful approaches that takes into consideration farmers of any kind from small-scale to big enterprises.
Following the geographical expansion is one of the most critical factors of market share positioning strategy in the FaaS markets. Producers develop new markets for their products not just in the home country but abroad as well to leverage the prospects of global demand for organic and eco-friendly products and agricultural processes. A central knowledge being the interpretation of local agricultural methods, climatic situations plus exact market needs is the key for successful expansion. Through, FaaS providers gain a diversified customer base by setting an international presence and also nurture their status as leaders with a multi-dimensional, local farming context view.
To make the market be aware about the new FaaS solution and inform current market about the advantages it offers, effective marketing and communication strategies are needed. Providers invest resources into strategic marketing campaigns pushing the benefits of time and resource savings, sustainability and financial gains. One of the strategies we can use to grow thought leadership is through our participation at events and workshops held in the agricultural industry and also through publication. This will give us reputation and position us as leaders in matters FaaS. The message of the simplification of the integration process and the proliferation of the positive impact on agriculture noted in the market education and acceptance assists with the communication.
Combining operating models that are based on the adjustment to the industry trends, the regulatory changes and the technology novelty constantly will give a guarantee for a prolonged success of the Farming as a Service market. Providers must stay abreast of advancements in precision agriculture, automation, and sustainable farming practices. Regular updates to their platforms to incorporate new technologies and enhance service capabilities ensure long-term relevance and competitiveness.

















Leave a Comment