Market Analysis
Europe PV Inverter Market (Europe, 2025)
Introduction
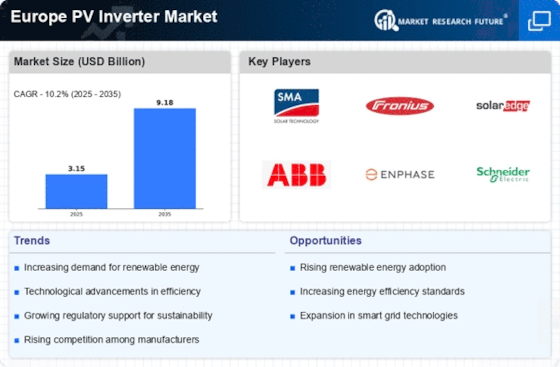
In Europe, the photovoltaic inverter market is expected to grow significantly as a result of the region’s focus on energy independence and green energy. Demand for photovoltaic (PV) systems, especially in the residential and commercial sectors, is on the rise. The trend is being bolstered by government support, technological developments, and growing awareness of the advantages of solar energy. The photovoltaic inverter is an essential component in the system. It converts the direct current (DC) generated by the solar cells into alternating current (AC) for use in households and industry. The changing relationship between energy generation and consumption in Europe and the innovations in inverter technology will influence the market dynamic and the competitive landscape.
PESTLE Analysis
- Political
- By the year 2025 the Green Plan of the European Union, aims at reducing by 55% the amount of the emissions of the greenhouse gases as compared with the year ’90, and it is on the basis of this reduction that the promotion of the use of all the forms of energy, especially the solar, is being carried out. For this purpose the European Union has earmarked approximately one thousand billions of re for the promotion of sustainable investments, amongst which is the promotion of the projects and the construction of the solar energy and its related structures. In addition to this, in several of the member States there are in place subsidies and feed-in tariffs, which in Germany for example reach up to eight cents per kilowatt-hour.
- Economic
- The European inverter market is influenced by the general economic climate. The European Commission expects the European economy to grow by 2.1% in 2025. This growth is expected to increase investments in the field of green energy, including inverters. Also, the average price of a solar photovoltaic system in Europe will fall by about 30% from 2020 to 2025. The average cost of a residential photovoltaic system will be about € 1,200 per kW in 2025, which makes solar energy more accessible to consumers and companies.
- Social
- In Europe, the awareness of the need for a change to a sustainable economy has grown dramatically. Recent polls have shown that over 75% of Europeans support a shift to a renewable energy system as a way of combating climate change. It is estimated that by 2025 around 40% of European households will have installed solar systems, which will increase the demand for inverters. The trend towards energy independence is also promoting the installation of inverters and solar panels, as individuals look to reduce their dependence on conventional energy.
- Technological
- The use of inverters is expected to increase the efficiency and performance of the photovoltaic system by 2025. In this case, the average efficiency of the string inverters is expected to reach 98.5%, while the efficiency of the microinverters is expected to reach 97%. The use of smart inverters, which can communicate with the network and optimize energy use, will become more common. By 2025, about one quarter of new photovoltaic systems will have these advanced inverters. This change is expected to increase the overall reliability and functionality of the photovoltaic system.
- Legal
- In 2025, the framework for the European inverter market will be set by the European Commission's Renewable Energy Directive, which stipulates that by then at least 32% of the total energy consumed in the EU must come from renewable sources. The compliance with these regulations is crucial for manufacturers and operators of photovoltaic inverters. In addition, the EU will probably introduce new regulations on energy efficiency and safety. All inverters will have to meet the IEC 62109 safety standard.
- Environmental
- The enviromental impact of photovoltaic inverters is becoming an increasingly important issue, and as the EU strives for a circular economy by 2025, the enviromental impact of PV inverters is becoming an increasingly important issue. To ensure that 85% of waste from photovoltaics is recycled, the enviromental impact of photovoltaic inverters is directly influenced by the disposal of photovoltaic panels. Also, the enviromental impact of manufacturing photovoltaic inverters is being reviewed, with the aim of reducing the CO2 emissions in production by 30 % by 2025. The enviromental benefits of solar energy, a reduction of around one billion tons of CO2 annually in Europe, illustrate the importance of photovoltaic inverters in achieving a circular economy.
Porter's Five Forces
- Threat of New Entrants
- The barriers to entry in the European PV inverter market in 2025 are moderate. The market is growing due to increasing demand for renewable energy, but the barriers to entry are high, because of the high level of capital investment, the need for high-level technical knowledge and the need to comply with strict regulations. Brand loyalty and customer recognition are high among the established companies, which can deter new entrants. However, technological development and the enabling regulatory environment can encourage new entrants.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- Suppliers have low bargaining power in the Europe PV inverter market due to the presence of many manufacturers and the easy availability of a variety of products. The market is characterized by the presence of a wide range of suppliers offering different components, which limits the influence of any single supplier. Supplier power has also been weakened by the trend toward vertical integration among some manufacturers, as companies seek to reduce their dependence on external suppliers.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers
- The buyers in the Europe photovoltaic inverter market are in a strong position to negotiate due to the increasing number of choices available and the competitive nature of the market. There are many similar products from different suppliers and it is easy to switch suppliers if there are better prices or features. Also, buyers are becoming more informed and demanding as a result of the growing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency, which is strengthening their bargaining position.
- Threat of Substitutes
- The threat of substitutes in the Europe PV inverter market is moderate. There are other energy solutions such as batteries and other alternative energy systems, but the unique function of PV inverters to convert solar energy into usable electricity makes them somewhat unique. However, as technology evolves and new energy solutions emerge, the threat of substitutes will increase, and manufacturers will have to keep up with innovation and differentiation.
- Competitive Rivalry
- Competition in the Europe PV inverter market is intense, mainly because of the presence of many established players and new entrants. The companies compete with one another through aggressive marketing strategies, product innovations, and price competition. The rapid growth of the renewable energy sector and the increasing adoption of solar energy are also increasing the competition. The companies are focusing on developing newer products and improving their customer services to gain a competitive advantage.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- Strong regulatory support for renewable energy initiatives across Europe.
- Technological advancements leading to higher efficiency and lower costs of PV inverters.
- Growing consumer awareness and demand for sustainable energy solutions.
Weaknesses
- High initial investment costs for solar PV systems including inverters.
- Dependence on government incentives which may fluctuate.
- Limited availability of skilled labor for installation and maintenance.
Opportunities
- Expansion of solar energy projects driven by EU climate goals.
- Emerging markets within Eastern Europe showing potential for growth.
- Increased investment in energy storage solutions complementing PV inverter technology.
Threats
- Intense competition leading to price wars among manufacturers.
- Potential supply chain disruptions affecting component availability.
- Changing regulatory landscapes that could impact market dynamics.
Summary
The Europe photovoltaic inverter market will be characterized by strong government support and technological advancements that enhance efficiency and reduce costs. The market will also be constrained by high initial investment costs and a reliance on government subsidies. Opportunities for growth will include new emerging markets and the integration of energy storage solutions. Threats will include intensifying competition and supply disruptions. Strategic focus on innovation and market expansion will be crucial for companies to thrive in this environment.

















Leave a Comment