Market Share
Introduction: Navigating the Competitive Landscape of Distributed Energy Resource Management
The competition in the field of distributed energy resources is becoming more and more fierce. The key players, such as manufacturers, IT companies, and equipment companies, as well as the new AI companies, are vying for leadership with the help of cutting-edge technology such as AI analysis, IoT integration, and automation. The key to this is not only the improvement of efficiency, but also the alignment with the public's desire for sustainable and resilient energy. North America and Europe have a great opportunity to grow, and are now being driven by favorable policies and green building construction. However, the key players are still in China, Japan, and Southeast Asia. They are aiming for the next big thing. The C-level leaders need to be aware of these changes and be able to seize the opportunities in the industry.
Competitive Positioning
Full-Suite Integrators
These vendors offer comprehensive solutions that integrate various aspects of distributed energy resource management.
| Vendor | Competitive Edge | Solution Focus | Regional Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
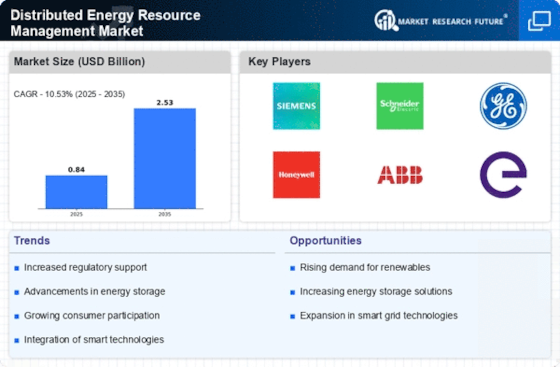
| ABB | Strong global presence and expertise | Energy management systems | Global |
| Schneider Electric | Innovative energy management solutions | Energy management and automation | Global |
| Siemens | Robust digital solutions for energy | Smart grid and energy management | Global |
| General Electric | Diverse energy portfolio and technology | Grid solutions and energy storage | Global |
Specialized Technology Vendors
These vendors focus on niche technologies that enhance distributed energy resource management capabilities.
| Vendor | Competitive Edge | Solution Focus | Regional Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tesla | Innovative battery technology and EV integration | Energy storage and solar solutions | North America, Europe |
| Enphase Energy | Leading microinverter technology | Solar energy solutions | North America, Europe |
| Sungrow | Advanced inverter technology | Renewable energy inverters | Asia, Europe |
Infrastructure & Equipment Providers
These vendors supply essential infrastructure and equipment for distributed energy systems.
| Vendor | Competitive Edge | Solution Focus | Regional Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eaton | Comprehensive power management solutions | Power distribution and management | Global |
| Johnson Controls | Integrated building and energy solutions | Building management systems | Global |
| Honeywell | Smart building technologies | Energy efficiency and management | Global |
| Cisco Systems | Networking solutions for energy systems | IoT and connectivity solutions | Global |
| NREL | Research-driven energy solutions | Renewable energy research and development | United States |
| Competitive Energy Services | Expertise in energy market analytics | Energy consulting and management | United States |
Emerging Players & Regional Champions
- Enel X (Italy): Offers demand response solutions and energy storage systems, recently partnered with local utilities in Italy to enhance grid flexibility, challenging established vendors like Siemens by providing more localized and agile solutions.
- Sonnen (Germany): Specializes in residential energy storage and virtual power plants, recently expanded its market presence in the U.S. with new installations, complementing Tesla's offerings by focusing on community-based energy sharing.
- Octopus Energy (UK): Provides innovative energy tariffs and smart grid technology, recently secured a contract with the UK government for a large-scale demand-side response program, positioning itself as a challenger to traditional energy suppliers.
- Power Ledger (Australia): Focuses on blockchain-based energy trading platforms, recently implemented pilot projects in several Australian cities, complementing existing energy management systems by enabling peer-to-peer energy trading.
- GridX (Germany): Offers software solutions for optimizing energy consumption in commercial buildings, recently partnered with several large retailers to implement energy management systems, challenging established players like Schneider Electric.
Regional Trends: By 2024, there is a considerable rise in the use of distributed energy resources in Europe and North America, mainly because of the need for grid stability and the regulatory support. Besides that, the technology specialization is shifting towards more integrated solutions that combine energy storage, demand response and smart grids. The focus is on solutions that are sustainable and involve the local community.
Collaborations & M&A Movements
- Together with Enel X, Siemens is developing a series of integrated energy management solutions that enhance the grid’s resilience and optimize energy consumption for commercial customers, thereby strengthening their position in the growing DER market.
- NextEra Energy, Inc., has acquired a majority interest in a leading energy storage company to strengthen its portfolio of renewable energy solutions and increase its market share in the distributed energy resources sector, at a time when the regulatory support for energy storage technology is growing.
- The remit of Schneider Electric and Tesla was to develop a combined product, combining Schneider’s energy management software with the batteries of the American company. The aim was to provide a comprehensive solution for the consumers of electricity, both domestic and commercial.
Competitive Summary Table
| Capability | Leading Players | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Forecasting | Enel X, Siemens | Enel X uses advanced machine learning algorithms to accurately predict energy demand. It uses this in its work with different distribution companies to optimize the grid. The platform from Siemens offers real-time data analysis to improve energy management. |
| Grid Integration | Schneider Electric, GE Renewable Energy | Schneider Electric's EcoStruxure is the platform that integrates distributed energy resources (DERs) into the existing grid. It has been used in several smart city projects. GE's focus is on scalable, resilient solutions for offshore wind farms. |
| Demand Response Management | EnerNOC, AutoGrid | With its unified and real-time load management system, EnerNOC has been able to achieve strong demand response performance. This has been proven by its successful collaboration with large commercial clients. In its recent case studies, the company has reported significant energy savings for the electric utility. |
| Energy Storage Solutions | Tesla, LG Chem | Energy storage with the Powerwall and Powerpack systems is widely used in both commercial and residential applications, and many of these systems have already been installed to increase energy resilience. The lithium-ion battery is recognized as an advanced energy storage technology, and it has provided a scalable solution for various markets. |
| Sustainability Reporting | IBM, SAP | The IBM Environmental Intelligence System has a comprehensive reporting system to help businesses monitor and reduce their carbon footprints. The system has been used by many Fortune 500 companies. As an integrated solution, SAP has a range of compliance and reporting tools for companies. |
| Customer Engagement Platforms | Oracle, Salesforce | Oracle's customer engagement cloud enables utility companies to enhance their customer relationships and satisfaction through targeted communications strategies. This has been proven by the success of several Oracle Cloud implementations in different utility companies. Case studies demonstrate improved customer retention. |
Conclusion: Navigating the Distributed Energy Landscape
DERMS is a highly competitive and fragmented market. DERMS is a market with many players, both established and new. The market is growing, but it is also becoming increasingly complex. In terms of geographical trends, there is a strong focus on the concept of sustainability, which is especially important in North America and Europe. This trend is reflected in the strategies of the DERMS vendors. The established vendors are using their existing IT systems to develop advanced capabilities, such as artificial intelligence and automation, to improve the efficiency of their operations. The new vendors are focusing on flexibility and innovation to gain market share. Artificial intelligence and automation will become increasingly important in the future as the market evolves. The vendors that can harness these capabilities and demonstrate their ability to focus on sustainable development will be the ones that are best able to take advantage of the opportunities offered by the rapidly changing environment.

















Leave a Comment