Rising Demand for Advanced Materials
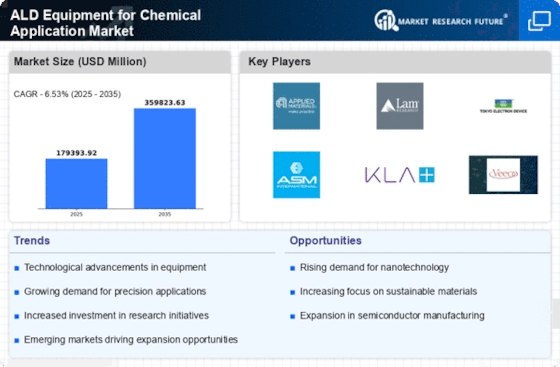
The ALD Equipment for Chemical Application Market is significantly influenced by the rising demand for advanced materials that require precise deposition techniques. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and telecommunications are increasingly seeking materials with superior properties, such as enhanced durability and conductivity. ALD technology is particularly suited for these applications due to its ability to create thin films with atomic-level precision. As a result, the market for ALD equipment is projected to grow, with estimates suggesting a value of USD 900 million by 2025. This demand for advanced materials not only drives innovation within the ALD Equipment for Chemical Application Market but also encourages collaboration between equipment manufacturers and material scientists to develop new solutions that meet industry standards.
Investment in Research and Development
Investment in research and development is a crucial driver for the ALD Equipment for Chemical Application Market. As companies strive to innovate and improve their product offerings, significant resources are being allocated to R&D initiatives. This focus on innovation is leading to the development of next-generation ALD equipment that offers enhanced performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Furthermore, partnerships between academic institutions and industry players are fostering advancements in ALD technology, which is likely to result in new applications and improved processes. The market is expected to benefit from these investments, with a projected growth rate of around 12% annually over the next few years. Thus, the commitment to R&D is a vital factor propelling the ALD Equipment for Chemical Application Market forward.
Technological Advancements in ALD Equipment
The ALD Equipment for Chemical Application Market is experiencing a surge in technological advancements that enhance the efficiency and precision of atomic layer deposition processes. Innovations such as improved precursor delivery systems and advanced monitoring techniques are being integrated into ALD equipment, allowing for better control over film thickness and uniformity. This is particularly relevant in sectors like semiconductor manufacturing, where the demand for high-quality thin films is paramount. As a result, the market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 15% over the next five years, driven by these technological improvements. Furthermore, the introduction of automation and machine learning in ALD processes is likely to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity, thereby attracting more investments into the ALD Equipment for Chemical Application Market.
Sustainability and Environmental Regulations
The increasing emphasis on sustainability and stringent environmental regulations is shaping the ALD Equipment for Chemical Application Market. Manufacturers are under pressure to adopt greener technologies and processes that minimize waste and reduce harmful emissions. ALD equipment is inherently more efficient in material usage compared to traditional deposition methods, which aligns well with sustainability goals. As industries strive to meet regulatory requirements, the demand for ALD equipment is expected to rise. For instance, the market for ALD equipment is anticipated to reach USD 1.2 billion by 2026, as companies seek to implement eco-friendly practices. This trend not only supports environmental initiatives but also enhances the reputation of companies within the ALD Equipment for Chemical Application Market, making sustainability a key driver of growth.
Diverse Application Growth in Various Industries
The ALD Equipment for Chemical Application Market is witnessing diverse application growth across multiple sectors, including electronics, energy, and healthcare. In the electronics sector, the demand for miniaturized components necessitates the use of ALD for precise thin film deposition. Similarly, in the energy sector, ALD is being utilized for the development of advanced battery technologies and solar cells, which require high-performance materials. The healthcare industry is also exploring ALD for coating medical devices to enhance biocompatibility. This broadening of applications is expected to propel the market forward, with projections indicating a market size of approximately USD 1 billion by 2025. The versatility of ALD technology is thus a significant driver for the ALD Equipment for Chemical Application Market, as it adapts to the evolving needs of various industries.