Emerging Markets
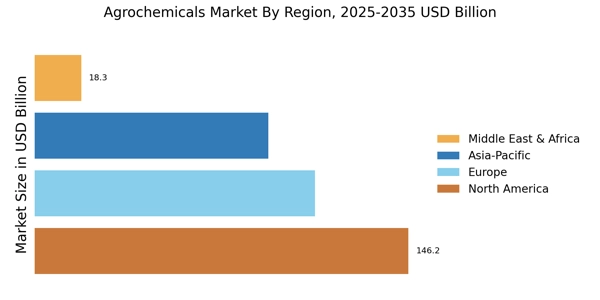
Emerging markets are presenting new opportunities for the Agrochemicals Market. Countries with developing agricultural sectors are increasingly adopting modern farming techniques, which often include the use of agrochemicals to enhance productivity. As these markets grow, the demand for agrochemicals is expected to rise significantly. For example, regions in Asia and Africa are witnessing a shift towards commercial agriculture, leading to increased investments in agrochemical products. This trend is supported by government initiatives aimed at boosting agricultural output and ensuring food security. Consequently, the Agrochemicals Market is likely to see substantial growth in these emerging regions, driven by the need for effective agricultural solutions.
Rising Food Demand
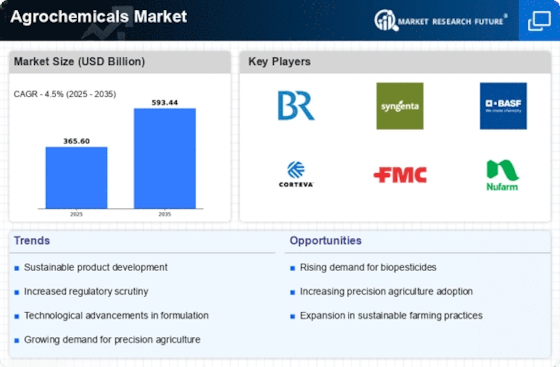
The Agrochemicals Market is experiencing a surge in demand driven by the increasing global population and the corresponding need for food production. As the world population is projected to reach approximately 9.7 billion by 2050, the pressure on agricultural systems intensifies. This necessitates the use of agrochemicals to enhance crop yields and ensure food security. According to recent estimates, the demand for agrochemicals is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of around 4.5% over the next few years. This growth is largely attributed to the need for higher productivity in agriculture, which is essential to meet the nutritional needs of a growing population. Consequently, the Agrochemicals Market is likely to expand significantly as farmers seek effective solutions to maximize their output.
Regulatory Frameworks
The regulatory frameworks governing the Agrochemicals Market are becoming more stringent, influencing product development and market dynamics. Governments are implementing stricter regulations regarding the use of agrochemicals, particularly concerning safety and environmental impact. This has led to increased research and development efforts among manufacturers to comply with these regulations while still meeting market demands. For instance, the introduction of new registration processes for agrochemical products can extend the time to market, impacting supply chains. However, these regulations also encourage innovation, as companies strive to create safer and more effective agrochemical solutions. As a result, the Agrochemicals Market is likely to adapt to these regulatory changes, fostering a more responsible approach to agrochemical use.
Sustainability Initiatives
Sustainability initiatives are becoming increasingly important within the Agrochemicals Market. As consumers and regulatory bodies demand more environmentally friendly practices, agrochemical manufacturers are responding by developing sustainable products. This includes the formulation of biopesticides and biofertilizers that are less harmful to the ecosystem. The market for sustainable agrochemicals is projected to grow significantly, with estimates suggesting a potential increase of over 10% annually. This shift not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also addresses the concerns of consumers who are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of conventional agrochemicals. Consequently, the Agrochemicals Market is likely to evolve, focusing on sustainable solutions that meet both agricultural productivity and environmental stewardship.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements play a pivotal role in shaping the Agrochemicals Market. Innovations such as precision agriculture, biotechnology, and digital farming are transforming traditional farming practices. The integration of data analytics and IoT devices allows farmers to optimize the use of agrochemicals, thereby enhancing efficiency and reducing waste. For instance, the adoption of drones for crop monitoring and the use of AI for predictive analytics are becoming increasingly prevalent. These technologies not only improve crop management but also contribute to sustainable practices by minimizing the environmental impact of agrochemicals. As a result, the Agrochemicals Market is likely to witness a shift towards more sophisticated and efficient agrochemical solutions, catering to the evolving needs of modern agriculture.