-
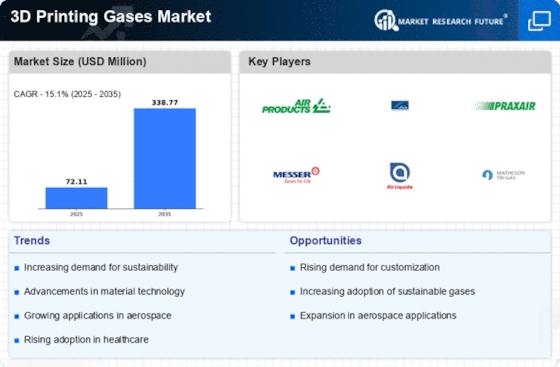
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
-
MARKET ATTRACTIVENESS ANALYSIS
- GLOBAL 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY GAS
- GLOBAL 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY FUNCTION
- GLOBAL 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY
- GLOBAL 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY END-USER
-
MARKET INTRODUCTION
-
DEFINITION
-
SCOPE OF THE STUDY
-
MARKET STRUCTURE
-
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
-
RESEARCH PROCESS
-
PRIMARY RESEARCH
-
SECONDARY RESEARCH
-
MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION
-
TOP DOWN &BOTTOM UP APPROACH
-
FORECAST MODEL
-
LIST OF ASSUMPTIONS
-
MARKET INSIGHTS
-
MARKET DYNAMICS
-
INTRODUCTION
-
DRIVERS
- RAPID GROWTH OF 3D PRINTING MARKET
- INCREASING DEMAND FOR 3D PRINTING GASES FROM THE AEROSPACE AND HEALTHCARE INDUSTRIES
- DRIVERS IMPACT ANALYSIS
-
RESTRAINTS
- RISING COST OF 3D PRINTING GASES
- RESTRAINTS IMPACT ANALYSIS
-
OPPORTUNITIES
- ADOPTION OF 3D PRINTING IN THE OIL & GAS INDUSTRY
-
IMPACT ANALYSIS OF COVID-19 ON 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET
-
MARKET FACTOR ANALYSIS
-
SUPPLY/VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS
- RAW MATERIAL SUPPLIERS
- CABLE MANUFACTURERS
- THIRD PARTY PROCUREMENT AGENTS/TRADERS BROKERS
- END USERS/ INDUSTRIES
-
PORTER’S FIVE FORCES MODEL
- THREAT OF NEW ENTRANTS
- BARGAINING POWER OF SUPPLIERS
- BARGAINING POWER OF BUYERS
- THREAT OF SUBSTITUTES
- INTENSITY OF RIVALRY
-
PRICING ANALYSIS
-
GLOBAL 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY GAS
-
OVERVIEW
-
ARGON
- ARGON: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- ARGON: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
NITROGEN
- NITROGEN: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- NITROGEN: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
GAS MIXTURES
- GAS MIXTURES: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- GAS MIXTURES: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
GLOBAL 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY
-
OVERVIEW
-
STEREOLITHOGRAPHY
- STEREOLITHOGRAPHY: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- STEREOLITHOGRAPHY: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
LASER SINTERING
- LASER SINTERING: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- LASER SINTERING: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
POLY-JET
- POLY-JET: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- POLY-JET: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
MATERIAL JETTING
- MATERIAL JETTING: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- MATERIAL JETTING: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
ELECTRON BEAM MELTING
- ELECTRON BEAM MELTING: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- ELECTRON BEAM MELTING: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
OTHERS
- OTHERS: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- OTHERS: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
GLOBAL 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY FUNCTIONS
-
OVERVIEW
-
INSULATION
- INSULATION: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- INSULATION: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
COOLING
- COOLING: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- COOLING: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
ILLUMINATION
- ILLUMINATION: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- ILLUMINATION: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
GLOBAL 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY END-USER
-
OVERVIEW
-
AUTOMOTIVE
- AUTOMOTIVE: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- AUTOMOTIVE: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
AEROSPACE & DEFENSE
- AEROSPACE & DEFENSE: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- AEROSPACE & DEFENSE: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
CONSUMER PRODUCTS
- CONSUMER PRODUCTS: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- CONSUMER PRODUCTS: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
HEALTHCARE
- HEALTHCARE: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- HEALTHCARE: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
OTHERS
- OTHERS: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
- OTHERS: MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST BY REGION/COUNTRY, 2018-2030
-
GLOBAL 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY REGION
-
OVERVIEW
-
NORTH AMERICA
- U.S.
- CANADA
-
EUROPE
- GERMANY
- FRANCE
- UK
- ITALY
- SPAIN
- RUSSIA
- REST OF EUROPE
-
ASIA PACIFIC
- CHINA
- JAPAN
- INDIA
- AUSTRALIA & NEW ZEALAND
- REST OF ASIA PACIFIC
-
LATIN AMERICA
- BRAZIL
- MEXICO
- ARGENTINA
- REST OF LATIN AMERICA
-
MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA
- TURKEY
- SOUTH AFRICA
- NORTH AFRICA
- GCC COUNTRIES
- REST OF MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA
-
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
-
INTRODUCTION
-
COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING
-
KEY PLAYERS MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS
-
COMPANY PROFILES
-
BASF SE
- COMPANY OVERVIEW
- PRODUCTS OFFERINGS
- FINANCIAL DETAILS
- SWOT ANALYSIS
- KEY STRATEGIES
-
LINDE PLC
- COMPANY OVERVIEW
- PRODUCTS OFFERINGS
- FINANCIAL DETAILS
- SWOT ANALYSIS
- KEY STRATEGIES
- RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
-
AIR LIQUIDE
- COMPANY OVERVIEW
- PRODUCTS OFFERINGS
- FINANCIAL DETAILS
- SWOT ANALYSIS
- KEY STRATEGIES
- RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
-
AIR PRODUCTS AND CHEMICALS, INC.
- COMPANY OVERVIEW
- PRODUCTS OFFERINGS
- FINANCIAL DETAILS
- SWOT ANALYSIS
- KEY STRATEGIES
- RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
-
NIPPON SANSO HOLDINGS CORPORATION
- COMPANY OVERVIEW
- PRODUCTS OFFERINGS
- FINANCIAL DETAILS
- SWOT ANALYSIS
- KEY STRATEGIES
-
SOL GROUP
- COMPANY OVERVIEW
- PRODUCTS OFFERINGS
- FINANCIAL DETAILS
- SWOT ANALYSIS
- RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
-
MESSER GROUP
- COMPANY OVERVIEW
- PRODUCTS OFFERINGS
- FINANCIAL DETAILS
- SWOT ANALYSIS
-
UNIVERSAL INDUSTRIAL GASES, INC.
- COMPANY OVERVIEW
- PRODUCTS OFFERINGS
- SWOT ANALYSIS
-
OTHER COMPANIES
-
APPENDIX
-
REFERENCES
-
RELATED REPORTS
-
LIST OF TABLES
-
LIST OF ASSUMPTIONS
-
ARGON MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
ARGON MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
NITROGEN MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
NITROGEN MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
GAS MIXTURES MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
GAS MIXTURES MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
STEREOLITHOGRAPHY MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
STEREOLITHOGRAPHY MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
LASER SINTERING MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
LASER SINTERING MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
POLY-JET MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
POLY-JET MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
MATERIAL JETTING MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
MATERIAL JETTING MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
ELECTRON BEAM MELTING MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
ELECTRON BEAM MELTING MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
OTHERS MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
OTHERS MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
INSULATION MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
INSULATION MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
COOLING MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
COOLING MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
ILLUMINATION MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
ILLUMINATION MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
AUTOMOTIVE MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
AUTOMOTIVE MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
AEROSPACE & DEFENSE MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
AEROSPACE & DEFENSE MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
CONSUMER PRODUCTS MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
CONSUMER PRODUCTS MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
HEALTHCARE MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
HEALTHCARE MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
OTHERS MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
OTHERS MARKET ESTIMATES & FORECAST, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
GLOBAL 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
GLOBAL 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY REGION, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
NORTH AMERICA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
NORTH AMERICA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
NORTH AMERICA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY GAS, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
NORTH AMERICA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY GAS, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
NORTH AMERICA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
NORTH AMERICA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
NORTH AMERICA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY FUNCTIONS, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
NORTH AMERICA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY FUNCTIONS, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
NORTH AMERICA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY END-USER, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
NORTH AMERICA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY END-USER, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
U.S.: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY GAS, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
US: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY GAS, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
US: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
US: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
US: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY FUNCTIONS, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
US: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY FUNCTIONS, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
US: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY END-USER, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
US: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY END-USER, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
CANADA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY GAS, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
CANADA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY GAS, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
CANADA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
CANADA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
CANADA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY FUNCTIONS, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
CANADA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY FUNCTIONS, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
CANADA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY END-USER, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
CANADA: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY END-USER, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
EUROPE: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2018-2030(USD MILLION)
-
EUROPE: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2018-2030(TONS)
-
EUROPE: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY GAS, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
EUROPE: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY GAS, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
EUROPE: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
EUROPE: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
EUROPE: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY FUNCTIONS, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
EUROPE: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY FUNCTIONS, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
EUROPE: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY END-USER, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
EUROPE: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY END-USER, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
GERMANY: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY GAS, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
GERMANY: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY GAS, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
GERMANY: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
GERMANY: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
GERMANY: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY FUNCTIONS, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
GERMANY: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY FUNCTIONS, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
GERMANY: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY END-USER, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
GERMANY: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY END-USER, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
FRANCE: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY GAS, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
FRANCE: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY GAS, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
FRANCE: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
FRANCE: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2030 (TONS)
-
FRANCE: 3D PRINTING GASES MARKET, BY FUNCTIONS, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
-
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- North America Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- North America Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- North America Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- North America Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- North America Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- US Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- US Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- US Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- US Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- US Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- Canada Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Canada Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Canada Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Canada Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Canada Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- Europe Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Europe Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Europe Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Europe Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Europe Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- Germany Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Germany Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Germany Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Germany Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Germany Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- France Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- France Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- France Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- France Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- France Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- UK Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- UK Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- UK Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- UK Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- UK Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- ITALY Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Italy Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Italy Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Italy Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Italy Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
-
- Spain Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Spain Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Spain Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Spain Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Spain Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- Rest Of Europe Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Rest of Europe Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Rest Of Europe Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Rest of Europe Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Rest of Europe Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- Asia-Pacific Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Asia-Pacific Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Asia-Pacific Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Asia-Pacific Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Asia-Pacific Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- China Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- China Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- China Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- China Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- China Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- Japan Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Japan Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Japan Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Japan Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Japan Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- India Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- India Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- India Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- India Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- India Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- Australia Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Australia Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Australia Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Australia Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Australia Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- Rest of Asia-Pacific Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Rest of Asia-Pacific Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Rest of Asia-Pacific Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Rest of Asia-Pacific Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Rest of Asia-Pacific Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- Middle East & Africa Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Middle East & Africa Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Middle East & Africa Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Middle East & Africa Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Middle East & Africa Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- Saudi Arabia Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Saudi Arabia Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Saudi Arabia Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Saudi Arabia Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Saudi Arabia Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- UAE Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- UAE Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- UAE Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- UAE Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- UAE Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- South Africa Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- South Africa Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- South Africa Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- South Africa Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- South Africa Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- Rest of Middle East & Africa Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Rest of Middle East & Africa Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Rest of Middle East & Africa Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Rest of Middle East & Africa Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Rest of Middle East & Africa Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- Latin America Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Latin America Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Latin America Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Latin America Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Latin America Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- Brazil Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Brazil Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Brazil Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Brazil Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Brazil Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- Argentina Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Argentina Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Argentina Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Argentina Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Argentina Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others
- Rest of Latin America Outlook (USD Million, 2019-2030)
- Rest of Latin America Floor coatings market by Gas
- Argon
- Nitrogen
- Gas Mixtures
- Rest of Latin America Floor coatings market by Function
- Insulation
- Cooling
- Illumination
- Rest of Latin America Floor coatings market by Technology
- Stereolithography
- Laser Sintering
- Poly-Jet
- Material Jetting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Others
- Rest of Latin America Floor coatings market by End User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Consumer Products
- Healthcare
- Others








Leave a Comment