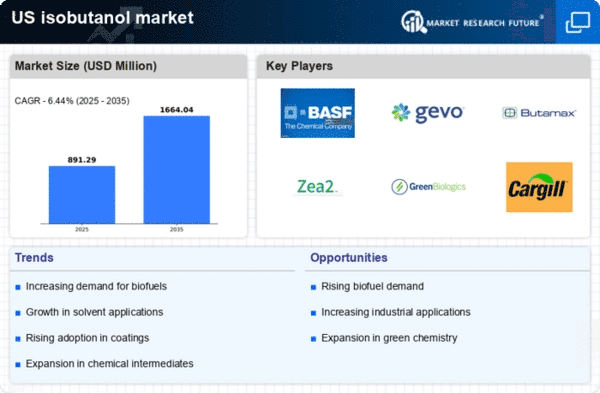
Growing Demand for Biofuels
The increasing emphasis on renewable energy sources is driving the demand for biofuels, including isobutanol. As the US government implements stricter regulations on greenhouse gas emissions, the isobutanol market is likely to benefit from this shift towards sustainable energy. In 2025, the biofuel market is projected to reach approximately $200 billion, with isobutanol playing a crucial role due to its favorable properties as a fuel additive. This growing demand for biofuels is expected to enhance the market dynamics of the isobutanol market, as consumers and industries seek cleaner alternatives to traditional fossil fuels.
Regulatory Support for Green Chemicals
The US government is actively promoting the use of green chemicals through various policies and incentives, which is likely to bolster the isobutanol market. Initiatives aimed at reducing reliance on petrochemicals and encouraging the adoption of bio-based products are gaining traction. For instance, the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) program supports the production of renewable fuels, including isobutanol, by providing financial incentives. This regulatory support is expected to create a favorable environment for the growth of the isobutanol market, as manufacturers align their production strategies with government mandates.
Rising Awareness of Environmental Impact
There is a notable increase in awareness regarding the environmental impact of traditional solvents and fuels, which is influencing consumer preferences towards greener alternatives. This trend is particularly relevant for the isobutanol market, as isobutanol is recognized for its lower toxicity and reduced environmental footprint compared to conventional solvents. As industries strive to meet sustainability goals, the demand for isobutanol is expected to rise. In 2025, the market for eco-friendly solvents is anticipated to grow by 15%, further solidifying the position of isobutanol as a preferred choice in various applications.
Expanding Applications in Chemical Manufacturing
Isobutanol is increasingly being utilized in various chemical manufacturing processes, which is propelling the growth of the isobutanol market. Its versatility as a solvent and intermediate in the production of chemicals such as butyl acrylate and isobutyl acetate is noteworthy. The chemical manufacturing sector in the US is projected to grow at a CAGR of 3.5% from 2025 to 2030, indicating a robust demand for isobutanol. This expansion in applications not only diversifies the market but also enhances the overall value proposition of the isobutanol market, as manufacturers seek efficient and effective chemical solutions.
Technological Innovations in Production Processes
Advancements in production technologies are playing a pivotal role in shaping the isobutanol market. Innovations such as fermentation processes and catalytic conversion methods are enhancing the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of isobutanol production. These technological improvements are likely to reduce production costs, making isobutanol more competitive against traditional solvents. As production techniques evolve, the isobutanol market is expected to witness increased output and improved product quality, which could attract a broader range of applications across various industries.