Market Analysis
In-depth Analysis of Pheochromocytoma Market Industry Landscape
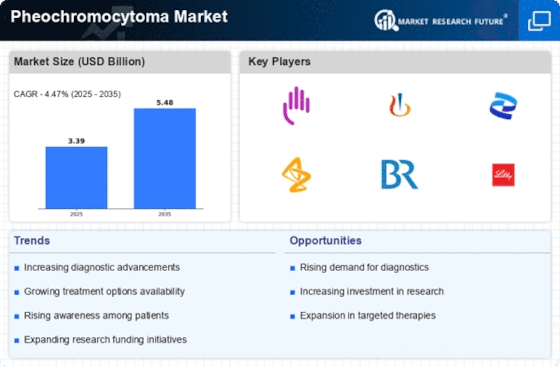
The market dynamics of pheochromocytoma, a rare neuroendocrine tumor that originates in the adrenal glands, are characterized by challenges in early diagnosis, advancements in diagnostic technologies, and ongoing efforts to improve treatment options. Pheochromocytomas are known for secreting excessive catecholamines, leading to a range of symptoms that necessitate specialized diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. The fact that the pheochromocytoma is a rare disease creates problems the market dynamics unique. However, a limited awareness can lead to delayed diagnosis focusing on the way of improvement which is education and design specialized diagnostic tools. Technological advancements in the field of diagnostic especially in the imaging techniques such as CT scans, MRI, functional imaging with MIBG scans have changed the face of the pheochromocytoma market. Such technologies assist in the accurate localization and characterization of the tumors; treatment can be quickly and effectively carried out. The discovery of genetic mutations connected to pheochromocytoma as those for the succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) gene family has put a remarkable effect on market dynamics. Genetics testing is of great importance for the detection of individuals at high risk destined for appropriate patient management concerning hereditary versions of diseases. The difficulties with diagnosing pheochromocytoma mostly depend on the symptom variability and episodic catecholamine release. Mishandling or delayed diagnosis results in serious complications which influences the need for better diagnostic mechanism and awareness programs market. Incontinuing research the attention is being drawn to the search for key biomarkers of pheochromocytoma blood-plasma and urine. The elucidation of the specific laboratory tests for detections of catechols amines and metanePhi1 NeFrins the ongoing market dynamics further providing the non – invasive and efficient diagnostic options. Surgical management of pheochromocytomas is a majorstill is pivotal in treatment. Advancements in surgical techniques, such as the laparoscopic and robot-assisted ones aimed at reducing invasiveness, improving recovery time and enhancing patient outcomes define the market landscape. However pharmacological management of pheochromocytoma includes application of anti-adrenergic blockers as well as beta-blockers. The market is driven by continuous research for the advancement towards the optimum use of drugs in order to improve treatment efficacy, and address issues related with side effects manifested by the prolong use of medication. The role of patient advocacy and support groups is quite huge in the market trends of pheochromocytoma. These organizations increase the level of awareness of the issues related to the problem, make special resources available to the patients and their families and, finally; promote communication between the facilitator and the patient community. Pheochromocytoma is a worldwide menace and market dynamics depends on regions. The issues faced by patients and healthcare providers in their daily lives are universal; the only variations can be observed on the basis of the viability of the healthcare infrastructure, access to specialized diagnostic services, and genetic patterns of disposition.
The future outlook for the pheochromocytoma market involves a multidimensional approach, encompassing advancements in diagnostics, treatment modalities, and patient care. As research progresses and awareness grows, the market is poised for improvements in early detection, personalized treatment approaches, and enhanced quality of life for individuals affected by this rare neuroendocrine tumor.

















Leave a Comment