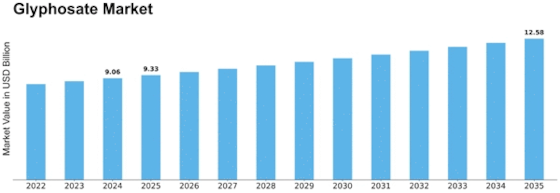
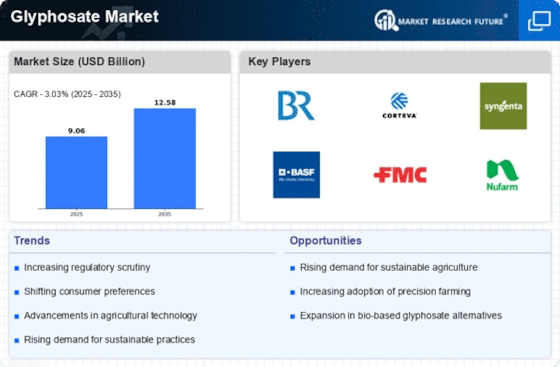
Glyphosate Size
Glyphosate Market Growth Projections and Opportunities
The Glyphosate Market, as a vibrant segment of the global agrochemical industry, is affected by diverse factors ranging from farming practices to regulatory policies. Glyphosate is an important herbicide that plays a major role in weed control and crop management. Genetically modified (GM) crops have been one of the key drivers in the market dynamics, which are characterized by no-till farming systems, glyphosate resistance, and the widespread use of glyphosate-tolerant GM crops. The increased adoption of glyphosate-tolerant genetically modified (GM) crops can also be said to drive the trends observed in this market. Glyphosates' market dynamics are significantly impacted by zero- or minimum-tillage type of farming approach, leading to a considerable decrease in soil tillage. The method of no-till agriculture does not disturb the ground much while killing weeds through herbicides like glyphosate. With this type of tillage, conservation occurs, saving moisture in soils, decreasing erosion, and helping carbon get sequestered into soils. Therefore, as farmers increasingly adopt such practices for sustainability purposes and improvements in soil structure, demand for glysophate remains high, thereby shaping its forces. However, concerns regarding herbicide resistance are now emerging as notable determinants for changes taking place within the Glyphosate Market. Prolonged use of glyphosate has resulted in certain kinds of weed plants being resistant to it, thus raising questions on whether it should still be used as an effective product based on how it was initially designed to function. As such, farmers are forced to implement integrated weed management schemes that involve other forms of herbicides besides chemical ones. Changes witnessed in relation to how these weeds were managed affect market dynamics because they do not rely on one type alone but rather increase demand for varied types. Regulatory dynamics play an essential role in defining how markets respond toward a given commodity like glysophate. Regulatory agencies have expressed concern over environmental and health effects that may arise from using the herbicide. Some countries have banned or limited the use of glysophate, while others dictate acceptable levels of residues. The price of glyphosate-based products is influenced by global economic factors such as commodity prices and exchange rate fluctuations. Consequently, farming decisions made by farmers are largely driven by economics, which affects market dynamics through cost dynamics with respect to weed control options since a farmer wants the most cost-effective means available. This makes the industry highly unstable because it operates within an economic landscape. Consumer perception and preferences regarding the safety of glyphosate and its potential impacts on human health and the environment are some of the reasons that have led to shifts in this market. In addition, advances in agricultural technology and the development of new formulations also influence trends within this market share. Manufacturers always try to develop new types of glysophate that can be more efficient, environmentally friendly, and safe for users' health. Underlying these complex forces are a number of dynamic powers that include GM crop adoption, no-till farming, concern over weed resistance, regulation changes, global economy conditions, consumer attitudes towards these chemicals shifting, technological breakthroughs in organic chemistry, among other things which shape this particular business climate into what it is today making it highly volatile and flexible at any moment in time.

















Leave a Comment