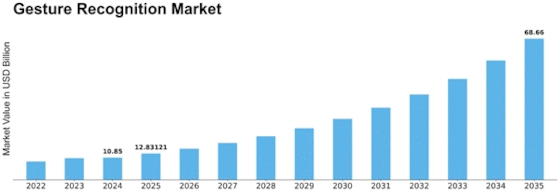
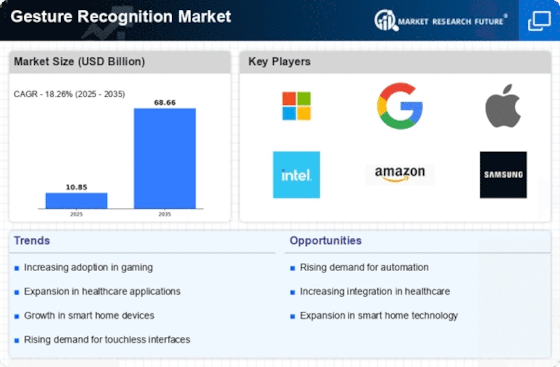
Gesture Recognition Size
Gesture Recognition Market Growth Projections and Opportunities
3D sensors, highly sensitive devices with diverse applications, play a pivotal role in various industries. The 3D sensor market is categorized based on technology, sensor type, and application. The technological classification encompasses projected-light sensors, stereo vision, time-of-flight sensors, and ultrasound. Projected-light sensors operate by focusing a narrow beam of light to capture a 3D image. Stereo vision, akin to human 3D sensing, is a widely adopted technology. Time-of-flight sensors determine distance by leveraging the known speed of light. In contrast, ultrasound sensors find popularity in robotic applications. The market for sensor types is further divided into acoustic sensors, accelerometer sensors, image sensors, and others. These diverse sensor types find implementation across a spectrum of applications, including consumer electronics, industrial settings, automotive, logistics, aerospace and defense, healthcare, and more.
The technology used in 3D sensors plays a crucial role in their functionality and applications. Projected-light sensors employ a focused light beam to capture detailed 3D images. This technology is particularly effective in applications where precision and accuracy are paramount. Stereo vision, inspired by the human visual system, is a widely embraced technology in the 3D sensor market. It relies on the principle of triangulation, utilizing the disparity between two images to perceive depth. This mirrors the human ability to perceive depth by processing images from two eyes. Stereo vision is instrumental in applications that require depth perception, such as robotics, autonomous vehicles, and certain industrial processes.
Time-of-flight sensors operate on the principle of measuring the time it takes for light to travel to an object and back. By utilizing the known speed of light, these sensors calculate distances with remarkable accuracy. This technology finds applications in various fields, including gesture recognition, gaming consoles, and robotics. Ultrasound sensors, on the other hand, employ sound waves to determine distances. These sensors are particularly favored in robotics, where precise distance measurements are crucial for navigation and object detection.
The sensor types used in 3D sensing technology are diverse, catering to specific functionalities and applications. Acoustic sensors, sensitive to sound waves, are utilized in applications such as audio recording and medical imaging. Accelerometer sensors measure acceleration forces and are commonly found in devices like smartphones for screen orientation. Image sensors capture visual information and are integral to applications such as cameras and facial recognition systems.
These varied sensor technologies and types have widespread applications across different industries. Consumer electronics leverage 3D sensors for applications like gaming consoles and virtual reality systems. In industrial settings, these sensors aid in automation, quality control, and robotics. The automotive industry benefits from 3D sensors in areas like collision avoidance and autonomous driving. Logistics, aerospace and defense, healthcare, and other sectors also incorporate 3D sensors to enhance their operational capabilities.
In summary, the 3D sensor market is characterized by its diverse technologies and sensor types, each tailored to specific applications across a range of industries. The continuous evolution of these sensor technologies contributes to advancements in various fields, driving innovation and improving the efficiency of diverse processes.

















Leave a Comment