

- Global Market Outlook
- In-depth analysis of global and regional trends
- Analyze and identify the major players in the market, their market share, key developments, etc.
- To understand the capability of the major players based on products offered, financials, and strategies.
- Identify disrupting products, companies, and trends.
- To identify opportunities in the market.
- Analyze the key challenges in the market.
- Analyze the regional penetration of players, products, and services in the market.
- Comparison of major players’ financial performance.
- Evaluate strategies adopted by major players.
- Recommendations
- Vigorous research methodologies for specific market.
- Knowledge partners across the globe
- Large network of partner consultants.
- Ever-increasing/ Escalating data base with quarterly monitoring of various markets
- Trusted by fortune 500 companies/startups/ universities/organizations
- Large database of 5000+ markets reports.
- Effective and prompt pre- and post-sales support.
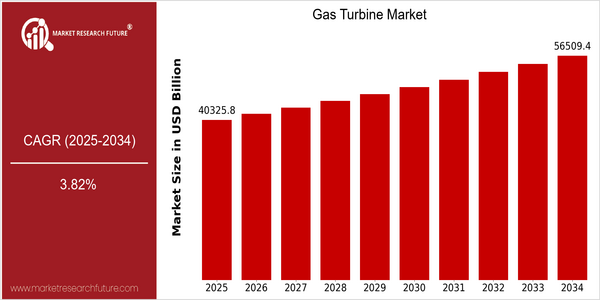
Market Size Snapshot
| Year | Value |
|---|---|
| 2025 | USD 40325.78 Billion |
| 2034 | USD 56509.45 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 3.82 % |
Note – Market size depicts the revenue generated over the financial year
The global gas turbine market is poised for significant growth, with a current market size projected at USD 40,325.78 billion in 2025 and an anticipated increase to USD 56,509.45 billion by 2034. This growth trajectory reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.82% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The steady expansion of the market can be attributed to several key factors, including the rising demand for cleaner energy sources, advancements in turbine technology, and the increasing need for efficient power generation solutions across various industries. Technological innovations, such as the development of high-efficiency gas turbines and hybrid systems, are driving the market forward. These advancements not only enhance performance but also reduce emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals. Major players in the gas turbine sector, including General Electric, Siemens, and Mitsubishi Power, are actively investing in research and development to introduce next-generation products. Strategic initiatives, such as partnerships for technology sharing and investments in renewable energy integration, further underscore the competitive landscape of the market, positioning these companies to capitalize on the growing demand for gas turbine solutions.
Regional Market Size
Regional Deep Dive
The Gas Turbine Market is experiencing significant growth across various regions, driven by increasing energy demands, technological advancements, and a shift towards cleaner energy sources. In North America, the market is characterized by a strong presence of leading manufacturers and a focus on natural gas as a primary fuel source. Europe is witnessing a transition towards renewable energy integration, while Asia-Pacific is rapidly expanding its infrastructure to support industrial growth. The Middle East and Africa are leveraging their abundant natural resources, and Latin America is gradually adopting gas turbines to enhance energy efficiency and reliability.
Europe
- The European Union's Green Deal aims to make Europe climate-neutral by 2050, prompting investments in gas turbine technology that can support the transition to hydrogen and other renewable fuels.
- Companies like Rolls-Royce and Ansaldo Energia are innovating in the gas turbine sector, focusing on hybrid systems that combine gas turbines with renewable energy sources to enhance grid stability.
Asia Pacific
- China is rapidly expanding its gas turbine capacity, with state-owned enterprises like China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC) investing in new projects to meet the growing energy demand and reduce coal dependency.
- India's government is promoting the use of gas turbines through initiatives like the National Gas Grid, which aims to enhance the country's gas infrastructure and improve energy access.
Latin America
- Brazil is exploring the use of gas turbines to enhance its energy mix, particularly in the context of its growing renewable energy sector, with companies like GE providing advanced turbine solutions.
- Regulatory frameworks in countries like Mexico are evolving to support private investment in gas infrastructure, which is expected to drive the adoption of gas turbines in power generation.
North America
- The U.S. is investing heavily in natural gas infrastructure, with companies like General Electric and Siemens leading the development of advanced gas turbine technologies that improve efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Regulatory changes, such as the Biden administration's push for cleaner energy, are encouraging the adoption of gas turbines in power generation, particularly in states like California and Texas, where renewable integration is a priority.
Middle East And Africa
- Countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE are investing in gas turbine technology as part of their Vision 2030 initiatives, focusing on diversifying their energy sources and reducing reliance on oil.
- The African Development Bank is funding projects that incorporate gas turbines to improve energy access in sub-Saharan Africa, highlighting the role of gas in supporting economic development.
Did You Know?
“Gas turbines can achieve efficiencies of over 60% when combined with combined cycle technology, making them one of the most efficient power generation technologies available today.” — International Energy Agency (IEA)
Segmental Market Size
The Gas Turbine Market segment is currently experiencing stable growth, driven by increasing energy demands and a shift towards cleaner energy sources. Key factors propelling this segment include the need for efficient power generation and stringent regulatory policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions. Technological advancements in turbine efficiency and emissions control are also significant drivers, enabling operators to meet both performance and environmental standards. Currently, the adoption stage of gas turbines is in the scaled deployment phase, with notable examples including GE's HA gas turbines and Siemens' SGT-800, which are widely used in power plants across North America and Europe. Primary applications include electricity generation in combined cycle power plants and industrial processes, particularly in sectors like oil and gas. Trends such as the global push for sustainability and government mandates for cleaner energy sources are accelerating growth in this segment. Additionally, innovations in digital twin technology and predictive maintenance are shaping the evolution of gas turbines, enhancing operational efficiency and reliability.
Future Outlook
The Gas Turbine Market is poised for steady growth from 2025 to 2034, with a projected market value increase from approximately $40.33 billion to $56.51 billion, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.82%. This growth trajectory is underpinned by the rising demand for efficient and reliable power generation solutions, particularly in emerging economies where industrialization and urbanization are accelerating. By 2034, it is anticipated that gas turbines will account for a significant share of the global power generation mix, with usage rates expected to rise from current levels, driven by the need for cleaner energy sources and the transition away from coal and oil-based power generation. Key technological advancements, such as the development of high-efficiency gas turbines and hybrid systems that integrate renewable energy sources, will play a crucial role in shaping the market landscape. Additionally, supportive government policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting energy efficiency are expected to further bolster market growth. The increasing focus on decarbonization and the adoption of natural gas as a transitional fuel will also enhance the attractiveness of gas turbines, particularly in regions where renewable energy infrastructure is still developing. As a result, the Gas Turbine Market is set to evolve significantly, driven by both technological innovation and regulatory frameworks that favor cleaner energy solutions.
Covered Aspects:| Report Attribute/Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size Value In 2022 | USD 14.01 Billion |
| Growth Rate | 6.2% (2022-2030)Base Year2021Market Forecast Period2022-2030Historical Data2018 & 2020Market Forecast UnitsValue (USD Billion)Report CoverageRevenue Forecast, Market Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and TrendsSegments CoveredCapacity, Technology, and RegionGeographies CoveredNorth America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Rest of the WorldCountries CoveredThe U.S, Canada, Germany, France, the UK, Italy, Spain, China, Japan, India, Australia, South Korea, and BrazilKey Companies ProfiledGeneral Electric (U.S.), Siemens (Germany), Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd. (Japan), Alstom S.A (France), Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. (Japan), Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited. (India), Ansaldo Energia, (Italy), Rolls-Royce Holdings plc. (U.K), Harbin Electric Company Limited. (China)Key Market OpportunitiesNew product launches and R&D Amongst major key PlayersKey Market DynamicsRevamp in electricity generation infrastructure to aggressively pursue gas-based power generation |
Gas Turbine Market Highlights:
Leading companies partner with us for data-driven Insights
Kindly complete the form below to receive a free sample of this Report
Tailored for You
- Dedicated Research on any specifics segment or region.
- Focused Research on specific players in the market.
- Custom Report based only on your requirements.
- Flexibility to add or subtract any chapter in the study.
- Historic data from 2014 and forecasts outlook till 2040.
- Flexibility of providing data/insights in formats (PDF, PPT, Excel).
- Provide cross segmentation in applicable scenario/markets.









