Market Analysis
In-depth Analysis of Antimicrobial Textile Additive Market Industry Landscape
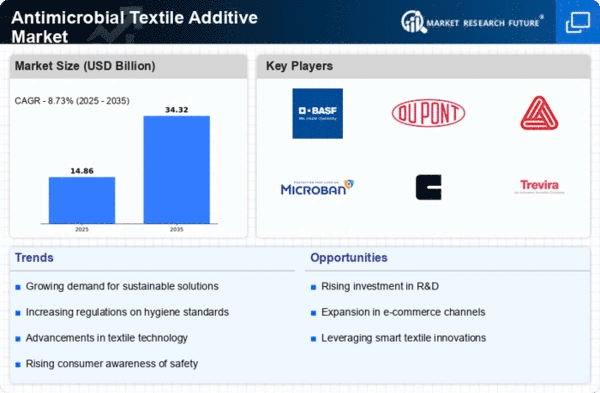
The dynamics of the antimicrobial textile additive market have been driven by increasing accentuation towards hygiene, health and safety across various sectors. Antimicrobial Textile Additives used to suppress microbial growths on fabric have now become an essential part of solving issues related to bacterial and viral contamination. One major factor that keeps pushing this market around is increased demand for antimicrobial textiles within healthcare settings especially against deadly viruses like COVID-19 pandemic has called for use of antibacterial agents among others on hospital linen, uniforms or other medical apparel so as to minimize infections caused by bacteria.
The dynamism characterizing the global markets dealing with the AMPs has been fueled by increasing awareness of these attributes beyond healthcare field (Isaac et al., 2019). Inclusion of anti-microbial chemicals in clothing costumer sports and home textiles has helped in reduction of odor caused by bacteria and fungi. These range from household products such as towels to clothes such as socks; an indication that people are aiming for hygienic textiles in their daily lives that will help them to improve their health. The last one is the increasing trend of antimicrobial additives in various end use applications due to the growing consumer preference for functional and hygienic textiles.
Another dynamic that changes with time is the focus on sustainability which has become an important aspect of this market. Manufacturers are developing antimicrobials derived from plants or animals as a way of minimizing environmental footprints associated with conventional agents (Triboulet et al., 2019). As we strive towards achieving global sustainability objectives, sustainable alternatives including bio-based or plant based additives are gaining popularity among conscious customers within the textile industry.
Antibiotic resistance globally and effective infection control methods drive demand for antimicrobial textile additives as well. Traditional antibiotics are facing challenges related to bacterial resistance hence textile manufacturers have looked at alternative mechanisms they can use to curb bacterial contamination (Ghasemi et al., 2017). Antimicrobial Additives make sure there are no chemicals released unlike traditional antibacterial treatments thereby acting as a sustainable solution to stop microbial growth on fabric.
Research and development also contributes significantly towards changing dynamics of antimicrobial textile additive market. This includes ongoing research aimed at development of highly advanced technologies such as nano-based additives which ensure durability, efficiency, safety among others. Application innovations and integration approaches target efficient ways where by different textile producers can incorporate anti-microbial chemicals into various fabrics easily.

















Leave a Comment