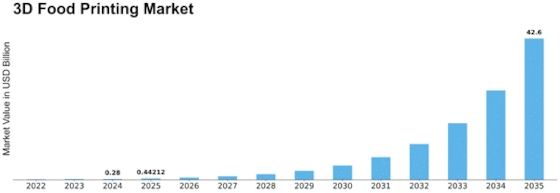
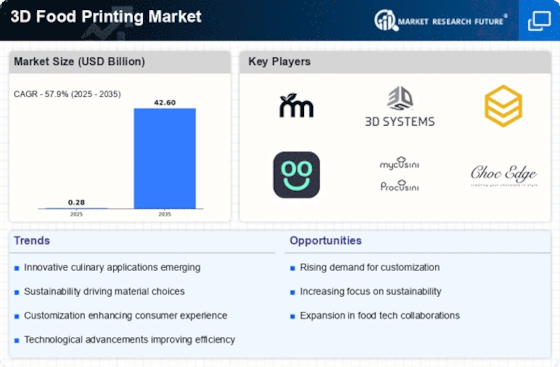
3d Food Printing Size
3D Food Printing Market Growth Projections and Opportunities
The 3D food printing market is influenced by a myriad of factors that collectively shape its dynamics. Technological advancements stand out as a primary driver, continually propelling the market forward. As 3D printing technology evolves, becoming more sophisticated and user-friendly, it enhances the capabilities of 3D food printing. Innovations in printing materials, precision, and speed contribute to the growing acceptance and adoption of this technology across the food industry. The pace of technological progress plays a pivotal role in determining the market's trajectory, with ongoing research and development pushing the boundaries of what is achievable in 3D food printing. Consumer preferences and behaviors are equally crucial market factors. The demand for personalized and customizable food options is on the rise, driven by a desire for unique culinary experiences. The ability of 3D food printing to cater to individual preferences, from shaping the aesthetics of food to tailoring nutritional content, aligns with this consumer trend. Additionally, as awareness of sustainability grows, consumers are seeking eco-friendly choices, and 3D food printing's potential to minimize food waste and use alternative, sustainable ingredients positions it as a solution that resonates with environmentally conscious consumers. Regulatory considerations are significant factors influencing the 3D food printing market. As this technology involves the production of consumables, regulatory bodies play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and quality of 3D printed food products. The establishment of clear and comprehensive regulatory frameworks is essential for building trust among consumers and industry stakeholders. Regulatory standards that address the safety of materials used in 3D printing, as well as the processes involved, contribute to the market's stability and long-term viability. Cost is a pivotal factor that can either propel or impede the adoption of 3D food printing. The initial investment required for 3D printing equipment and materials has been a barrier to entry for some businesses. However, as the technology matures, economies of scale and increased competition are expected to drive down costs, making 3D food printing more accessible to a broader range of companies. Cost considerations not only include the upfront expenses but also ongoing operational costs, such as maintenance and material expenses, which impact the overall feasibility and attractiveness of 3D food printing solutions. The competitive landscape and market dynamics are shaped by the strategic collaborations and partnerships between technology providers, food companies, and research institutions. These partnerships foster innovation by combining expertise from different domains, leading to the development of new applications and products. Collaborations also play a crucial role in addressing challenges and accelerating the commercialization of 3D food printing technologies. As the market continues to grow, the nature and success of these partnerships will significantly influence the overall competitiveness and innovation potential of the 3D food printing industry. Global economic trends and geopolitical factors can impact the 3D food printing market on a macro scale. Economic conditions can influence consumer spending patterns, affecting the demand for innovative and premium food products. Additionally, geopolitical factors such as trade policies and international relations can impact the supply chain and market accessibility for 3D printing technology and related materials. A stable and conducive global environment is essential for the sustained growth of the 3D food printing market

















Leave a Comment